Wave Theory-Wavefront by Huygen
Summary:
This passage discusses the concepts of wave optics, specifically focusing on Huygens’s wave theory and Newton’s corpuscular theory. The main points are as follows:
- Newton’s Corpuscular Theory:
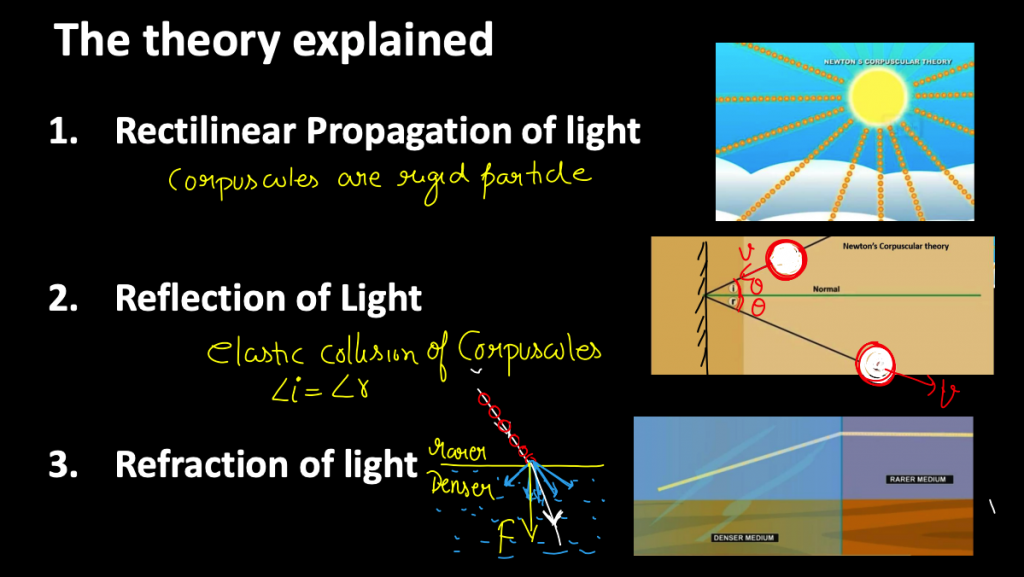
- Light sources emit tiny corpuscles (massless particles of different shapes and sizes).
- Corpuscles travel in straight lines with varying speeds in different mediums.
- Different colours of light are associated with different sizes of corpuscles.
- Explained rectilinear propagation, reflection, and refraction of light.
- Failed to explain interference, diffraction, and polarization.
- Incorrectly predicted faster light travel in water or glass compared to air.
- Huygen’s Wave Theory:
- Light is a mechanical wave requiring a medium for propagation.
- Proposed the existence of a highly elastic and untouchable medium called ether.
- Explained rectilinear propagation, reflection, refraction, interference, and diffraction.
- It could not explain polarization and the photoelectric effect.
- Huygens Principle:
- Wavefront is the locus of all points in a medium oscillating in the same phase.
- The wave propagation direction is perpendicular to the wavefront.
- Secondary wavelets are generated from each point on a wavefront and spread in all directions.
- The tangent enveloping secondary wavelets forward gives a new wavefront.
- The behaviour of Plane Wavefront on Reflection & Refraction:
- Demonstrated refraction and reflection of plane wavefronts using prisms, lenses, and mirrors.
The passage introduces these wave optics theories and their applications, discussing concepts like wavefront, and secondary wavelets, and how they explain different optical phenomena. It also mentions the opportunity to join a Telegram group for more related material.
Excerpt:
Wave Theory-Wavefront by Huygen
Newton’s Corpuscular Theory (1675):
- Every Light Source emits tiny corpuscles(elastic, rigid & massless particles of different shapes & sizes).
- Corpuscles travel in straight lines with different speeds in different mediums.
- Different colours of light have different sizes of corpuscles.
The Theory Explained:
- Rectilinear Propagation of light.
- Reflection of Light.
- Refraction of light.
It failed to explain the following:
i. Interference
ii. Diffraction
iii. Polarisation
It was wrongly predicted that light travels faster in water or glass than in air.

Reviews