VCE Specialist 3/4 Notes
Summary:
These VCE Specialist 3/4 Notes are a concise overview of the topics covered in a CAS Tinspire course. It includes discussions on vectors, covering properties, operations, resolution, and angles. Circular functions are explored, including radians, degrees, graphs, and special properties. Complex numbers explain Cartesian and polar forms, conversions, and polynomial factorization. The calculus section covers differentiation, concavity, rational function sketching, integration, area calculations, volume, differential equations, and related rates. Kinematics and dynamics are discussed, focusing on graphs of position, velocity, and acceleration, as well as constant acceleration. Probability topics include discrete and continuous probability density functions, binomial distribution, linear combinations of random variables, and confidence intervals. Hypothesis testing for means, one-tail and two-tail tests, and type I and II errors are also addressed.
Excerpt:
VCE Specialist 3/4 Notes
VECTORS ———————————————————————————————————4
Vector calculations ————————————————————————————————————- 4
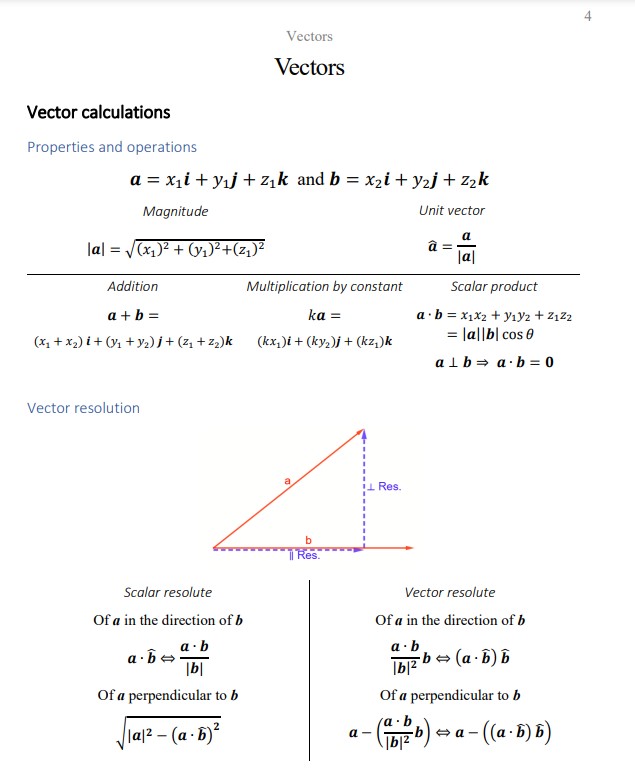
Properties and operations …………………………………………………………………………………………4
Vector resolution……………………………………………………………………………………………………..4
Linear dependence and collinearity …………………………………………………………………………….5
Vector angles…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..6
Vector functions—————————————————————————————————————– 7
CIRCULAR FUNCTIONS —————————————————————————————-8
Radians and degrees———————————————————————————————————– 8
Exact values and reference angles—————————————————————————————– 8
Graphs of circular functions ————————————————————————————————- 9
General solutions ————————————————————————————————————- 12
Special properties————————————————————————————————————- 12
Pythagorean identities…………………………………………………………………………………………….12
Complementary and symmetry properties………………………………………………………………….12
Groupings……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..12
Angle formulas—————————————————————————————————————– 13
Addition and subtraction of angles ……………………………………………………………………………13
Double angles………………………………………………………………………………………………………..13
COMPLEX NUMBERS —————————————————————————————- 14
Cartesian form —————————————————————————————————————– 14
Modulus and conjugates………………………………………………………………………………………….14
Converting between polar and Cartesian forms…………………………………………………………..14
Polar form———————————————————————————————————————– 15
Argand diagram representations of operations ——————————————————————— 15
Polynomial factorization over complex numbers ——————————————————————- 16
Sketching locus of z———————————————————————————————————– 17
CALCULUS —————————————————————————————————– 18
Differentiation —————————————————————————————————————– 19
Second derivative and concavity ……………………………………………………………………………….19
Sketching rational functions……………………………………………………………………………………..20
𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑥𝑐𝑥 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….20
Implicit differentiation…………………………………………………………………………………………….21
Antidifferentiation———————————————————————————————————— 22
Graphs of derivatives and antiderivatives …………………………………………………………………..22
Integration by substitution ………………………………………………………………………………………22
Partial fractions………………………………………………………………………………………………………23
Integration ———————————————————————————————————————- 25
The area between curves and axes………………………………………………………………………………….25
Evaluating definite integrals using inverse function ……………………………………………………..26
The volume of solid of revolution……………………………………………………………………………………27
Length of curve………………………………………………………………………………………………………28
Differential equations ——————————————————————————————————- 29
Verify differential equations …………………………………………………………………………………….30
Related rates …………………………………………………………………………………………………………31
Evaluating 𝑓(𝑥) using definite integral……………………………………………………………………….32
Euler’s method ………………………………………………………………………………………………………32
Slope field……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..33
KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS —————————————————————————— 34
Kinematics ———————————————————————————————————————- 34
Graphs of position, velocity and acceleration………………………………………………………………34
Representations of acceleration ……………………………………………………………………………….34
Constant acceleration……………………………………………………………………………………………..34
Dynamics———————————————————————————————————————— 35
PROBABILITY ————————————————————————————————– 36
Probability content from Methods 3/4——————————————————————————— 36
Discrete probability density function 𝑝(𝑥) ………………………………………………………………….36
Binomial distribution ………………………………………………………………………………………………36
Continuous probability density function 𝑓(𝑥)……………………………………………………………..37
Linear combinations of random variables—————————————————————————– 39
Distribution of sample means in normal distribution————————————————————– 40
Central limit theorem ……………………………………………………………………………………………..40
Normal approximation to binomial distribution…………………………………………………………..40
Confidence intervals for the population mean ………………………………………………………………….41
Hypothesis testing for the mean —————————————————————————————– 42
H0 and H1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………42
p-value, z-test and α ……………………………………………………………………………………………….42
One-tail and two-tail tests ……………………………………………………………………………………….42
Type I and Type II errors ………………………………………………………………………………………….43

Reviews