VCE PE Unit 1 Notes
Summary:
The VCE PE Unit 1 Notes provide an overview of the first chapter and second chapters of VCE PE Unit 1 Notes, which cover the topics of physical activity, sport and exercise, and the musculoskeletal system. The first chapter discusses the domains and dimensions of physical activity, as well as enablers and barriers to physical activity. The second chapter focuses on the structure and function of the musculoskeletal system, including ligaments, cartilage, tendons, and bones. The chapter also covers the functions of the skeletal system, synovial joints, joint movements, and anatomical terms such as levers.
Excerpt:
VCE PE Unit 1 Notes
AOS 1 – How does the musculoskeletal system work to produce movement?
CHAPTER 1 – Introduction to physical activity, sport and exercise
Physical activity – Physical activity is generally understood to be any bodily movement that uses the skeletal muscles and which expends energy.
VCE PE Unit 1 Notes
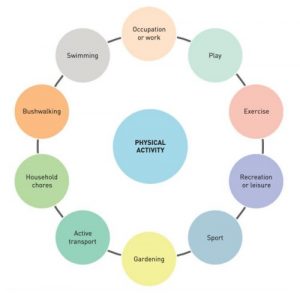
Domains of physical activity
– Leisure time
– Household/gardening
– Occupational
– Active transport
Dimensions of physical activity (FITT)
The FITT principle makes it possible to calculate the energy expenditure associated with physical activity.
– Frequency – The number of events of physical activity during a specific time period
– Intensity – The physiological effort associated with participating in a special type of physical activity
– Time (Duration) – The time of participation in a single bout of physical activity
– Type – The sort of physical activity that is being done
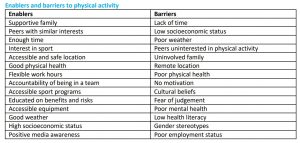
VCE PE Unit 1 Notes
CHAPTER 2 – Structure and Function of the musculoskeletal system
Musculoskeletal system – Skeletal system (bones and joints) and the voluntary muscle system.
Ligaments – connects bone to other bones
Cartilage – ‘shock-absorbing’ gel between joints
Tendons – connects muscle to bones
Bones
Axial Skeleton – provides the main support for the body and includes the skull, vertebral column and rib cage
Appendicular Skeleton – made up of the limb bones and their ‘girdles’ which connect to the axial skeleton
Cervical Vertebrae – make up the neck and responsible for supporting the head
Thoracic Vertebrae – connect the rib cage to the spinal column and form a protective shield for the heart and lungs
Lumbar Vertebrae – largest of the vertebrae and have high weight-carrying capacity

Reviews