VCE Geography 3/4 Revision Notes (Grade A)
Summary:
Area of Study 1: Population Dynamics focuses on key geographical concepts and population dynamics. The concepts covered include population distribution and density, population dynamics, global population distribution, population density, world population growth, natural increase and decrease, birth rates and death rates, fertility rates, demographic dividend, spatial association, infant mortality, maternal mortality, life expectancy, ageing populations, dependency populations, population pyramids, and the demographic transition model.
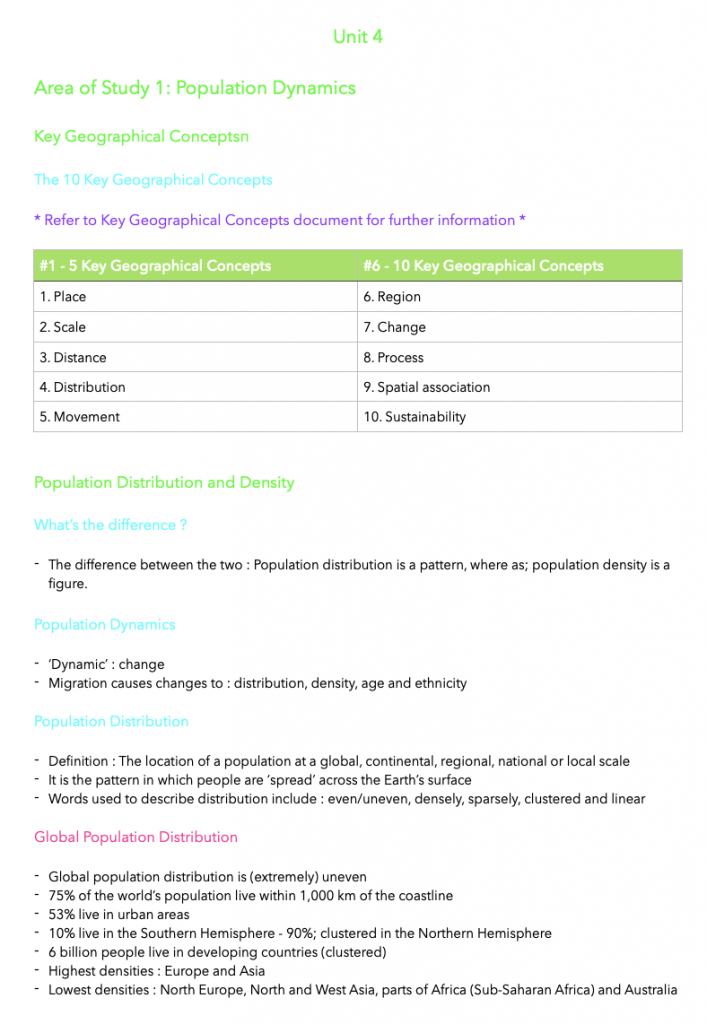
Population distribution refers to the pattern of people across different scales, while population density refers to the number of people in a specific area. Population dynamics refers to the changes in distribution, density, age, and ethnicity caused by factors like migration.
Global population distribution is uneven, with 75% living within 1,000 km of the coastline, 53% in urban areas, and 10% in the Southern Hemisphere. Developing countries have contributed the most to world population growth, with declining death rates being the main cause rather than increasing birth rates.
Birth rates and death rates are measured as crude birth rates (births per 1,000 people) and crude death rates (deaths per 1,000 people), respectively. Fertility rates indicate the average number of births per woman, with a rate of 2.1 considered replacement level. Declining fertility rates have been observed globally.
Infant mortality, maternal mortality, and life expectancy are important indicators of population health. Infant and under-five mortality rates have decreased, but disparities exist across regions. Life expectancy has increased globally, but there are significant variations between countries.
Ageing populations, characterized by a higher proportion of people aged 65 and older, are increasing globally. This trend has implications for healthcare, government support, and the economy. Dependency populations refer to those not in the workforce, including the elderly and children.
Population pyramids visually represent the age and sex structure of a population. Rapid growth, slow growth, and negative growth pyramids indicate different demographic patterns.
Excerpt:
VCE Geography 3/4 Revision Notes
Unit 4
Area of Study 1: Population Dynamics
Key Geographical Concepts
The 10 Key Geographical Concepts
* Refer to Key Geographical Concepts document for further information *
|
#1 – 5 Key Geographical Concepts |
#6 – 10 Key Geographical Concepts |
|
1. Place |
6. Region |
|
2. Scale |
7. Change |
|
3. Distance |
8. Process |
|
4. Distribution |
9. Spatial association |
|
5. Movement |
10. Sustainability |

Reviews