Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions (Grade A)
Summary:
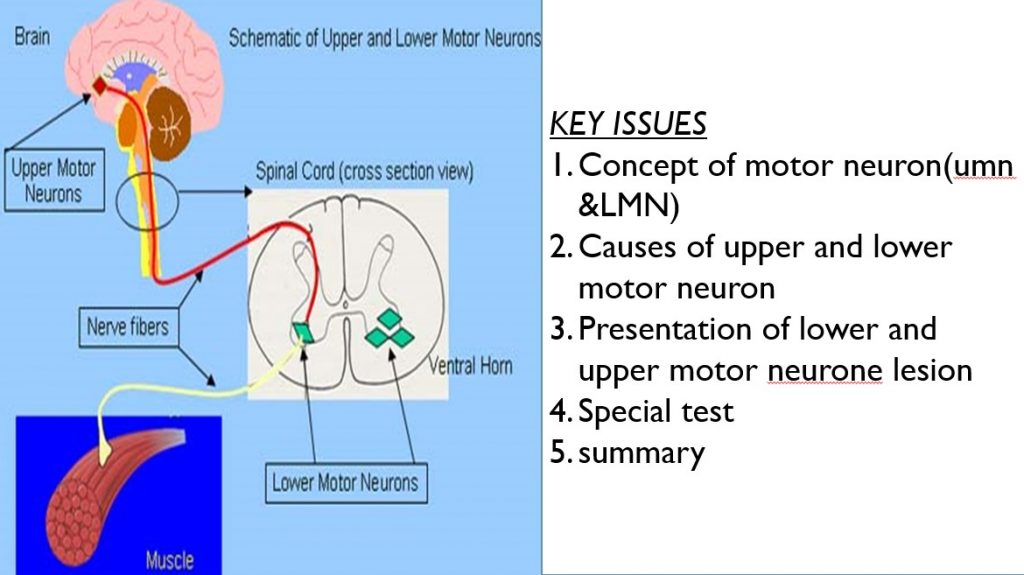
This presentation discusses upper and lower motor neuron lesions. Motor neurons are nerve cells responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system to muscles, facilitating movement through the release of neurotransmitters. Upper motor neurons (UMNs) originate in the cerebral cortex and travel to the brain stem or spinal cord, while lower motor neurons (LMNs) transmit signals from UMNs to the effector’s muscles for movement.
UMN lesions can be caused by conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, and vitamin B12 deficiency. These lesions can lead to a loss of voluntary control over muscles, resulting in disuse atrophy, increased muscle tone and reflexes, and decreased muscle strength. LMN lesions, on the other hand, can be caused by viruses like polio and West Nile, spinal muscular atrophy, and botulinum toxin. These lesions can lead to muscle atrophy, fasciculations, and decreased muscle tone, reflexes, and strength.
UMN and LMN lesions can be differentiated through special tests like the Babinski reflex test, pronator drift test, and Hoffmann sign, which can help diagnose and understand the extent of motor neuron damage.
Excerpt:
Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions (Grade A)
Motor Neuron
– Are the nerve cell responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system to ward the muscle and cause movement, and it facilitated by the release of neurotransmitters
- Upper motor neurone lesions prevent signals from travelling from the brain and spinal cord to specific muscle
- Muscles without this signal from the brain and spinal cord tend to be stiff and weak
There are two types of motor neurone-:
I. Upper motor neuron
ii. Lower motor neuron
Upper Motor Neuron
The upper motor neurone originates from the cerebral cortex and travels down to the brain stem or spinal cord
The upper motor neurone contains 2 pathway
1. Cortical spinal pathway –cortex to the spinal cord
2. Cortical bulbar – cortex to bulbar of the brain stem(pons, mid-brain, medulla)

Reviews