Types of Chemical Reactions
Summary:
The University of South Africa’s study unit, “Types of Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions”, guides students on balancing chemical equations and classifying various reaction types. It details several reactions, including Precipitation Reactions, where an insoluble precipitate forms when two solutions mix. Another reaction type is Acid-Base Reactions, involving hydrogen ion transfer between species, resulting in neutralization reactions. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions denote electron transfer, where oxidation equals electron loss and reduction to electron gain. Decomposition Reactions break a single substance into simpler ones, while Ionisation or Dissociation reactions occur when salts dissociate into ions in a solution. Combustion Reactions involve fuel and an oxidant, often oxygen, reacting to produce heat and light. The unit also covers Single and Double Displacement Reactions; the former is a redox reaction where an ion in solution is replaced via oxidation of a metallic element, while the latter involves ions or elements of two reactants exchanging partners to create two new compounds. The unit provides several examples of each reaction type and concludes with exercises to test students’ understanding.
Excerpt:
Types of Chemical Reactions
Types of Chemical Reactions; Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
STUDY UNIT 4 GENERAL CHEMISTRY UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH AFRICA
UNIT OUTCOMES
• Ability to write and balance chemical equations
• Ability to classify chemical reactions.
Types of chemical reactions
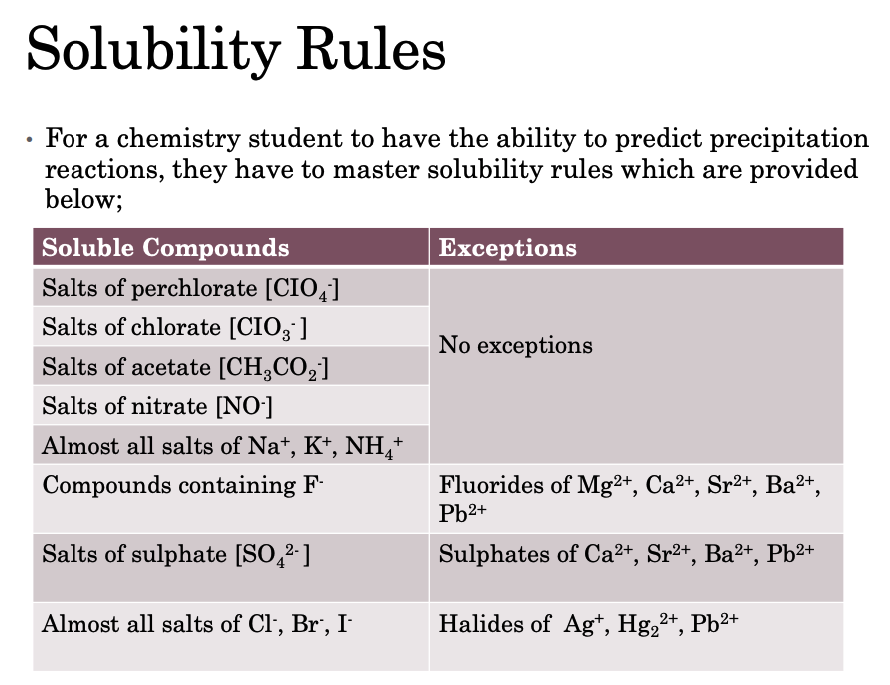
Precipitation Reactions & Solubility Rules
• In a precipitation reaction, a solid substance results when two solutions are mixed and also if and when one or more of the resulting products are insoluble.
• These insoluble products are known as precipitates.
• To represent the formation of a solid precipitate when writing a chemical equation, (s) or (↓) are used.
• Those substances which have relatively high solubility are known as soluble substances.
• The substances that have relatively low solubility are said to be insoluble. These kinds of substances readily precipitate from the solution.
• For a substance to precipitate, solution conditions should be such that its concentration surpasses its solubility

Reviews