Thermodynamics Notes for JEE Level
Summary:
The note provides an exhaustive insight into thermodynamics, discussing systems and their various types—open, closed, and isolated—based on their interactions with surroundings. It elaborates that a system can also be classified as homogeneous or heterogeneous based on phase uniformity. State functions like pressure, volume, and temperature are introduced to define a system’s state. Various processes such as isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, isochoric, and cyclic processes are detailed, each characterized by specific constant state variables. The first law of thermodynamics is introduced as energy conservation law, expressed mathematically as Δu = q + w, where Δu is the internal energy change, q is heat transfer, and w is work done.
The note also elucidates the concept of internal energy as the sum of all forms of energy a system can possess. Different modes of changing internal energy—through work, heat transfer, and matter transfer—are described. The importance of enthalpy, which combines internal energy and pressure-volume work, and its role in exothermic and endothermic reactions is highlighted. Extensive and intensive properties, as well as heat capacity, molar heat capacity, and specific heat capacity, are discussed for their significance in thermodynamics.
Excerpt:
Thermodynamics Notes for JEE Level
• Important Terms and Definitions
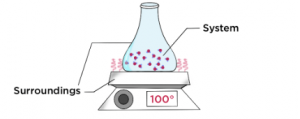
System: Refers to the portion of the universe that is under observation.
Surroundings: Everything else in the universe except the system is called surroundings. The Universe = The System + The Surroundings.
Thermodynamics Notes for JEE Level
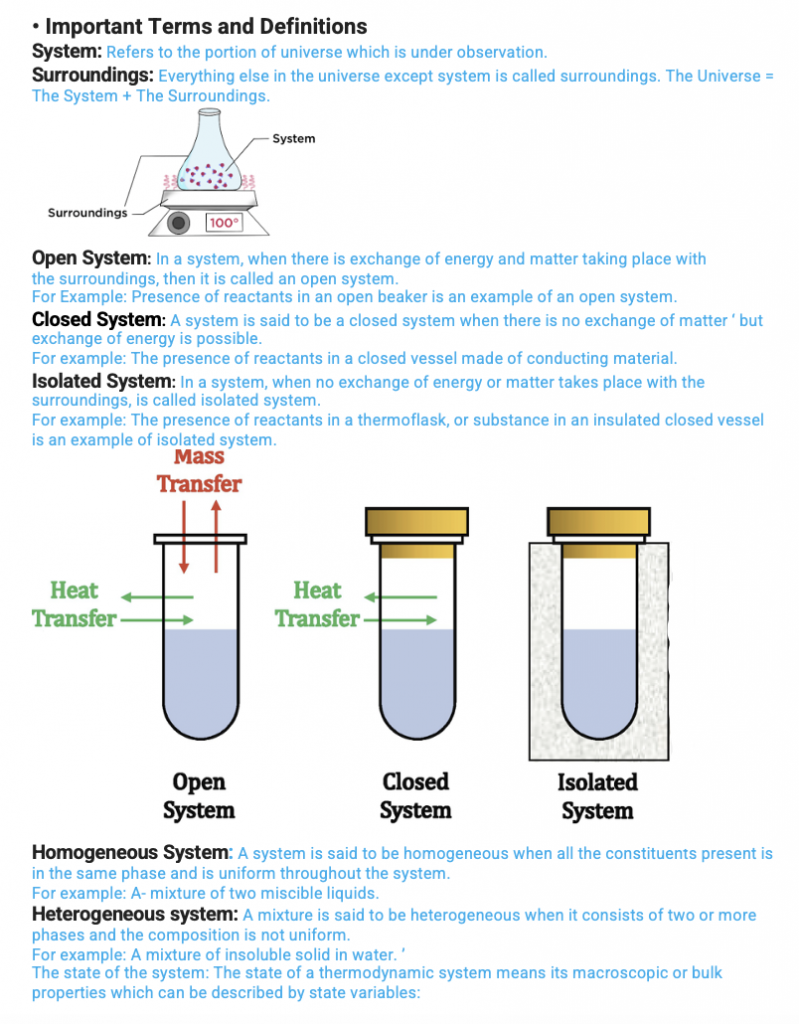
Open System: In a system, when there is an exchange of energy and matter taking place with
the surroundings, then it is called an open system.
For Example, Reactants in an open beaker are an example of an open system.
Closed System: A system is said to be closed when there is no exchange of matter ‘, but exchange of energy is possible.
For example, Reactants in a closed vessel made of conducting material.
Isolated System: In a system, where no exchange of energy or matter takes place with the surroundings, is called an isolated system.
For example, The presence of reactants in a thermoflask, or substance in an insulated closed vessel is an example of an isolated system.

Reviews