Supply and Demand Explained
Summary:
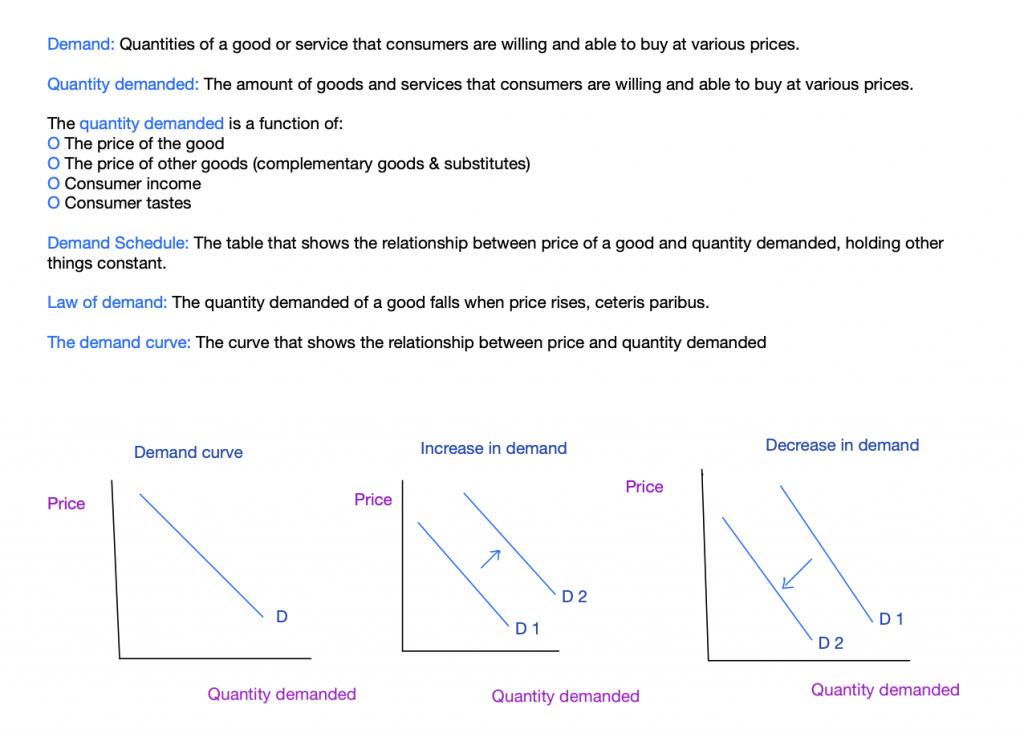
Demand refers to the quantities of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at different prices. Quantity demanded represents the specific amount of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to buy at varying prices. The quantity demanded is influenced by factors such as the price of the good, prices of other goods (complementary and substitute goods), consumer income, and consumer preferences.
The demand schedule is a table that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded while holding other factors constant. According to the law of demand, the quantity demanded decreases as the price of good rises, assuming other factors remain unchanged. The demand curve visually represents this relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Various factors can cause a shift in demand, including changes in consumer income, prices of related goods, consumer tastes and habits, expectations, and the number of buyers. Changes in price, on the other hand, only lead to movements along the demand curve.
Supply, on the other hand, refers to the quantity of goods and services that sellers are willing and able to offer at different prices. The quantity supplied represents the specific amount sellers are willing and able to sell at each price point. The law of supply states that the quantity supplied of a good increase as its price rises, assuming other factors remain constant. The supply curve visually depicts the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Factors that can lead to a change in supply include input costs, technology, expectations, and the number of sellers. Similar to demand, changes in price cause movements along the supply curve.
Excerpt:
Supply and Demand Explained
Demand: Quantities of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at various prices.
Quantity demanded: The number of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to buy at various prices.
The quantity demanded is a function of the following:
O The price of the good
O The price of other goods (complementary goods & substitutes)
O Consumer income
O Consumer tastes

Reviews