PHR2021 on How the Medicine Works
Summary:
The PHR2021 on How the Medicine Works note provides a comprehensive overview of various medication optimization and delivery topics. This insightful document covers a range of subjects, including optimizing dosage regimen design, liquid formulations, and excipients. It also delves into alternative formulations such as pates, paints, and gels for drug delivery. The note emphasizes the importance of modified-release oral and parenteral formulations in controlling drug release rates effectively. Additionally, it explores alternative routes of drug delivery and addresses the formulation and delivery challenges associated with macromolecules, which are large molecules used in medical treatments. “PHR2021 on How the Medicine Works” offers valuable insights into the advancements and complexities of medication delivery systems.
Excerpt:
PHR2021 on How the Medicine Works
DISCOVERY 1: OPTIMISING DOSAGE
REGIMEN DESIGN
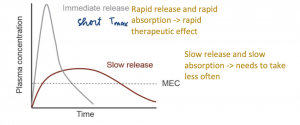
I. Dosage form
- For the drug to have effectiveness, they need to be absorbed into the systemic route.
Some factors have the ultimate impact on the rate and extent of systemic drug absorption, which are the route of administration, dosage form, and Physico-chemical properties of drugs - The oral formulation is the most common route.
- When tablets or capsules have good solubility and absorption, they exhibit therapeutic levels.
PHR2021 on How the Medicine Works
II. Physicochemical properties of drugs
- Applying Lipinski’s rule of 5, there are some important properties that drugs need to carry for an optimal drug absorption
o Log P <5
o Molecular weight > 500 Da
o No. of H-bond donors < 5
o No. of H-bond acceptor <10 - However, some biologics have very large molecular weight; they need to be a substrate of an influx
the transporter that is expressed at the small intestinal epithelial cell => for absorption - Moreover, even when drugs have all the optimal properties above, they still can have poor
absorption because of the high first-pass effect.
III. Route of administration -There are lots of routes to administer the medication:
o Vaginal
o Rectal
o Sublingual
o Buccal
o Nasal
o Pulmonary
o Transdermal
o Intravascular
o Subcutaneous
o Intravenous
o Ocular

Reviews