Overview of Anticoagulant Drugs (Grade A)
Summary:
The note provides a comprehensive summary of anticoagulant drugs, encompassing their drug subclasses, properties, mechanisms of action, adverse effects, indications, and dosage. In the realm of oral anticoagulants, Warfarin and Dicumarol are highlighted as coumarin compounds that function as vitamin K antagonists. These drugs exhibit a delayed onset of action and work by inhibiting the reduction of vitamin K, consequently preventing the synthesis of clotting factors. Warfarin, in particular, is indicated for thromboembolic conditions and requires careful dosage adjustment based on prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR) tests.
Excerpt:
Overview of Anticoagulant Drugs
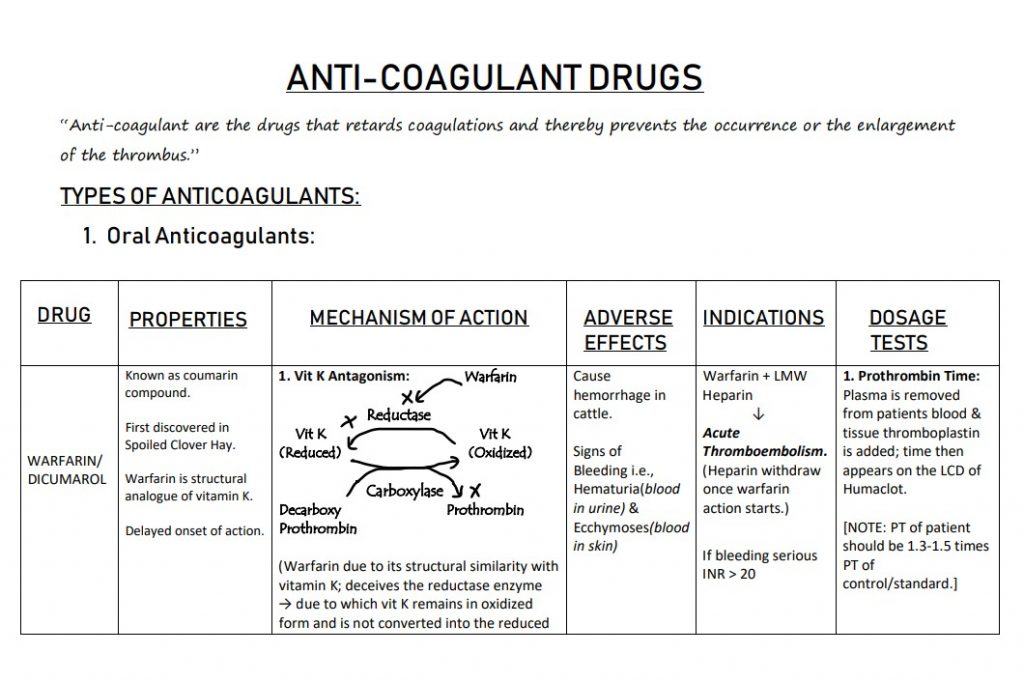
ANTI-COAGULANT DRUGS
“Anti-coagulant are the drugs that retards coagulations and thereby prevent the occurrence or the enlargement of the thrombus.”
TYPES OF ANTICOAGULANTS:
- Oral Anticoagulants:
| DRUG |
PROPERTIES |
MECHANISM OF ACTION |
ADVERSE EFFECTS |
INDICATIONS |
DOSAGE TESTS |
|
WARFARIN/ DICUMAROL |
Known as coumarin compound.
First discovered in Spoiled Clover Hay.
Warfarin is a structural analogue of vitamin K.
Delayed onset of action. |
1. Vit K Antagonism: Warfarin
Reductase Vit K Vit K (Reduced) (Oxidized)
Carboxylase Decarboxy Prothrombin Prothrombin
(Warfarin, due to its structural similarity with vitamin K; deceives the reductase enzyme → due to which vit K remains in oxidized form and is not converted into the reduced |
Cause hemorrhage in cattle.
Signs of Bleeding, i.e., Hematuria(blood in urine) & Ecchymoses(blood in skin) |
Warfarin + LMW Heparin
↓ Acute Thromboembolism. (Heparin withdraws once warfarin action starts.)
If bleeding serious INR > 20 |
1. Prothrombin Time: Plasma is removed from the patient’s blood & tissue thromboplastin is added; time then appears on the LCD of Humaclot.
[NOTE: PT of a patient should be 1.3-1.5 times PT of control/standard.] |
| form → & so the vit K clotting factors will not be synthesized.)
2. Trans-procoagulation Effect: (means against anticoagulant) Warfarin → inhibits protein C & S (endogenous anticoagulants which inhibit factor V & VIII )→ leads to activation of factor V & VIII. |
Several days required for coagulation factor level to return to normal after discontinue. |
Phytonadione (Vit K1 agonist)
↓ Indicated after coumarin compound discontinue for clotting factor recovery.
↓drug dosage ;dosage based on patient Prothrombin Time (PT). |
2. Internationalized Normalize Ratio:
INR= PT observed PT control͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟͟
ISI- International Sensitivity Index
ISI = 1.
INR = 2-3. |

Reviews