Multiple Beam Interferometry
Summary:
Interferometers are optical devices that exploit the principle of interference, most commonly in relation to light. There are various types of interferometers, including the Mach-Zehnder, Michelson, Fabry-Pérot, and Sagnac interferometers, each with unique configurations and applications. For instance, the Mach-Zehnder interferometer uses two beam splitters to split and recombine light beams, while the Michelson interferometer employs a single beam splitter. The Fabry-Pérot interferometer uses two parallel mirrors, allowing multiple round trips of light, and the Sagnac interferometer uses counter-propagating beams in a ring path. These devices can also be implemented using optical fibres, replacing beam splitters with fibre couplers. Interferometers have diverse applications, such as measuring distances with a high degree of accuracy, monitoring slight changes in optical wavelength, and characterizing light. However, they can be affected by mechanical and technical noise, which often necessitates the use of noise reduction techniques. Despite these challenges, interferometers remain indispensable tools in the realm of optical physics.
Excerpt:
Multiple Beam Interferometry
Interferometers
An interferometer is an optical gadget that uses the impact of interference. That should be possible with various types of radiation; however, this article explicitly manages optical interferometers, i.e., interferometers for light. Regularly, such a gadget depends on the accompanying activity rule: it begins with some input beams, parts it into two separate beams with a beam splitter of some sort or another (a to some degree transmissive mirror), potentially uncovers a portion of these beams to a few outer impacts (for example some length changes or refractive record changes in a transparent medium) and recombines the beams on another beam splitter. The power of the spatial shape of the resulting beam can then be utilized, for example, for estimation.
Interferometers, as often as possible, should be produced using high-quality optical components.
For instance, one frequently utilizes mirrors and optical flats with a high surface flatness.
Different types of interferometers.
Mach–Zehnder Interferometer.
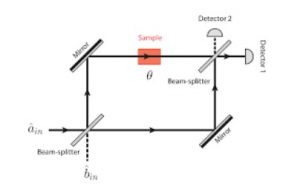
Multiple Beam Interferometry

Reviews