Microbiology and Immunology Notes
Summary:
The Microbiology and Immunology Notes provide comprehensive coverage of the MICR2000 course code, “Microbiology & Immunology,” offered at The University of Queensland. It covers the entire semester and includes 9 modules, which are Introduction to Microorganisms, Microbial Growth, Bacterial Pathogenesis, Virology, Environmental Microbiology, Mycology, Immunology, Vaccines and Viral Diagnostics, and Parasitology. Additionally, the note includes detailed explanations and illustrations for all the modules, which are separated into key concepts.
Excerpt:
Microbiology and Immunology Notes
Mid-Semester Examinable Content
Module 1 Introduction to Microorganisms
What is microbiology?
The study of microscopic living organisms: bacteria, archaea, viruses, fungi, algae, and protozoa.
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Some differences include the presence of a cell wall in prokaryotic cells, membrane-bound organelles, and intracellular compartments in eukaryotic cells.
What is cell morphology?
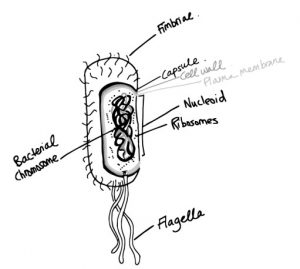
Cell morphology refers to size and shape. Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller than eukaryotic cells. Cocci (round/circular) and rods are common shapes of bacterial pathogens.
On top of this, cells that remain attached to each other can form distinctive patterns: pairs (diplococci), long chains (streptococci), 3D cubes (tetrads or Mid-Semester Examinable Content End-of-Semester Examinable Content MICR2000 Summary 2 sarcoma), or grape-like clusters (staphylococci). Filamentous bacteria are long, thin, rod-shaped bacteria that divide terminally and form long filaments composed of many cells attached end to end.
What are the key features of a bacterial cell wall?
Characteristics of all bacterial cells are metabolism (genetic and catalytic), growth (binary fission), and evolution. Some bacterial cells have additional characteristics: differentiations (spores), communication (chemical messengers), motility (flagellum), and genetic exchange.
Microbiology and Immunology Notes
Who were the key figures in the history of microbiology?
– Robert Hooke provided the first description of microbes.
– Antoni van Leeuwenhoek was the first to describe bacteria.
Louis Pasteur showed microbes are responsible for fermentation and disproved the theory of spontaneous generation. The Theory of Spontaneous Generation suggested living organisms arose spontaneously and randomly from non-living materials.

Reviews