Lubrication System in IC Engines
Summary:
This Lubrication System in IC Engines note provides an overview of lubrication systems in internal combustion engines. It covers the definition of lubrication, the purpose of lubrication, types of lubricants, properties of lubricants, engine parts that require frequent lubrication, and types of lubrication systems. The three types of lubrication systems discussed are mist lubrication, wet sump lubrication, and dry sump lubrication.
Excerpt:
Lubrication System in IC Engines
Definition of Lubrication
Lubrication is the action of applying a substance such as oil or grease to an engine or component so as to minimize friction and allow smooth movement.
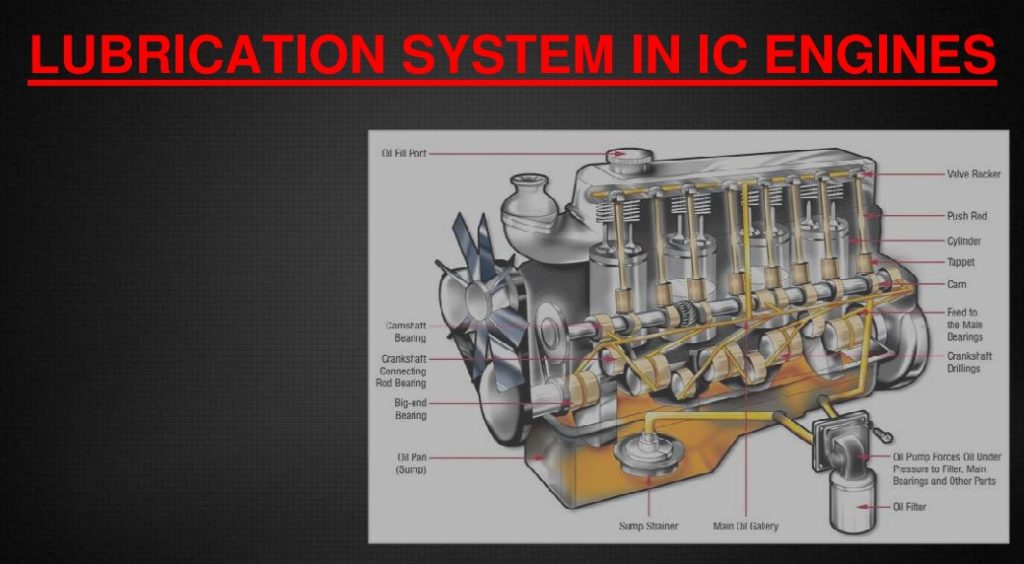
Lubrication System
A lubricating system is a mechanical system of lubricating internal combustion engines in which a pump forces oil into the engine bearings.
PURPOSE OF LUBRICATION
➢ To reduce the friction between moving parts
➢ To increase the efficiency
➢ To minimize the vibrations
➢ To reduce the corrosion and carbon deposits
➢ To reduce the heat of moving parts
➢ To minimize power loss due to friction
➢ To reduce the noise created by moving parts
➢ To provide cooling to the engine
TYPES OF LUBRICANTS
➢SOLID LUBRICANTS
➢ SEMI-SOLID LUBRICANTS
➢ LIQUID LUBRICANTS
PROPERTIES OF LUBRICANTS
➢ Viscosity
❑ It is a measure of the resistance to the flow of an oil
❑ It is measured in say bolt universal seconds (SUS)
❑ It is expressed in centistokes, centipoises, and redwood seconds
➢ Viscosity Index
❑ The viscosity of oil decreases with an increase in temperature
➢ Cloud point
❑ If oil is cooled, it will start solidifying at some time.
❑ The temperature at which oil starts solidifying is called the cloud point
PROPERTIES OF LUBRICANTS
➢Pour point
❑ It is the temperature just above which the oil sample will not flow under certain prescribed conditions
❑ this property is important for the operation of engines and substances at low-temperature conditions
➢ Flashpoint and Fire point
❑ The temperature at which the vapor of an oil flashes when subjected to a naked flame is called flashpoint
❑ The fire point is the temperature at which the oil, once lit with flame, will be burnt steadily at least for 5 seconds
➢ Specific Gravity
❑ It varies between 0.85 to 0.96

Reviews