Large Biological Molecules (Structure and Functions)
Summary:
This Large Biological Molecules note discusses the structure and function of large biological molecules. Macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are polymers built from monomers. Carbohydrates serve as fuel and building materials and include monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Lipids, though not true polymers are hydrophobic molecules with diverse structures, including fats, phospholipids, and steroids. Proteins are crucial to cell function, accounting for over 50% of the dry mass of most cells. They are constructed from 20 amino acids and serve as enzymes, catalyzing chemical reactions in the cell. Amino acids form polypeptides through peptide bonds, which fold into specific three-dimensional structures to create functional proteins.
Excerpt:
Large Biological Molecules (Structure and Functions)
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecule
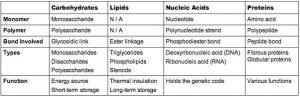
Large Biological Molecules
Lipids are not true polymers, they are large biological molecules.
Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers built from monomers
Macromolecules– Large carbohydrates( polysaccharides- a carbohydrate whose molecules consist of a number of sugar molecules bonded together.), proteins, and nucleic acids. The joining of smaller molecules forms a giant molecule.
Polymer– is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. Monomer-repeating units, or building blocks of a polymer, are smaller molecules. Some monomers have functions of their own.
In cells, chemical processes by which cells make polymers and break them down are facilitated by enzymes: A macromolecule serving as a catalyst, a chemical agent that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Most enzymes are proteins.
Condensation reaction- occurs when a monomer connects to another monomer or a polymer by covalent bonding with a loss of a smaller molecule.
If a water molecule is lost, the reaction is known as a dehydration reaction.
If during the process of breaking down a polymer into a monomer by the addition of a water molecule, the reaction is known as hydrolysis. EX: digestion.


Reviews