Income Taxation Notes
Summary:
This note covers Income and Income Taxation on Individuals. It discusses the nature and concept of income, provides an overview of income tax on individuals, and explores gains from dealings in property, capital, and ordinary assets. The note also distinguishes between purely compensation income earners and self-employed individuals. Additionally, it highlights income taxpayers with multiple employers.
Excerpt:
Income Taxation Notes
I. Nature and Concept of Income
Gross Income means all income derived from whatever source, including the following:
- Compensation for services in whatever form paid, including fees, salaries, wages, and commissions
- Income derived from the conduct of trade or business or the exercise of a profession
- Gains derived from dealings in property
- Interest
- Rents
- Royalties
- Dividends
- Annuities
- Prizes and winnings
- Pensions
- Partner’s distributive share from the net income of the general professional partnership
Income refers to the amount of money or its equivalent, representing gains or profit that flows into the taxpayer from whatever sources other than representing the return of capital.
| Taxable Income | Non-taxable Income |
| 1. Compensation | 1. Life insurance proceeds |
| 2. Business Income | 2. Return of premium |
| 3. Gains from property dealings | 3. Gifts, bequests, and devices |
| 4. Passive income | 4. Compensation for injuries |
| 5. Other taxable income | 5. Retirement benefits |
II. Income Tax on individuals (Overview)
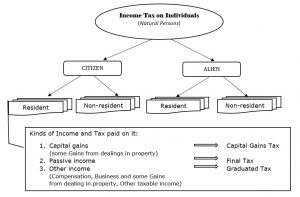
Income Taxation
The resident citizen is the only taxpayer who is taxable on his income within and outside the Philippines, while the rest are taxable for income within the Philippines only.
III. Gains from dealings in property, Capital, and Ordinary Assets
Gains from dealings in property are income derived from the sale or exchange of assets, either ordinary or capital. Gains represent the excess of the selling price over costs or other determinable value.
Classification of property:
- Ordinary Assets refer to:
- Stock in trade (inventory) of the taxpayer or other property of a kind that would properly be included in the inventory of the taxpayer if on hand at the end of the taxable year.
- Property used in trade or business of a character that is subject to the allowance for depreciation.
- Real property used in trade or business of the taxpayer.


Reviews