IGCSE Biology Variety of Organisms
Summary:
Living organisms are made up of cells, which are the fundamental structural units. It must perform eight essential life processes to be considered a living organism. Organisms are categorized into five kingdoms based on common ancestry. However, viruses are an exception and are not considered living organisms as they lack vital life processes and are not made of cells.
Yeast, unicellular fungi, is an essential organism used in baking and brewing due to its ability to respire aerobically and anaerobically. Mushrooms and moulds belong to the fungi kingdom as well. Mushrooms are a reproductive structure, while moulds have spores that grow into hyphae, breaking down food through saprotrophic nutrition.
Decomposers, including bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in recycling carbon by breaking down the remains of other organisms. Cells in multicellular organisms are specialized to carry out specific functions, known as cell differentiation. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into specialized cells.
Eukaryotic cells in plants and animals contain a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The movement of molecules and ions through membranes occurs through diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. The concentration gradient, temperature, distance, and surface area-to-volume ratio affect the diffusion rate. Active transport requires energy to move particles against a concentration gradient, facilitated by pumps in cell membranes.
Excerpt:
IGCSE Biology Variety of Organisms
Variety of Organisms
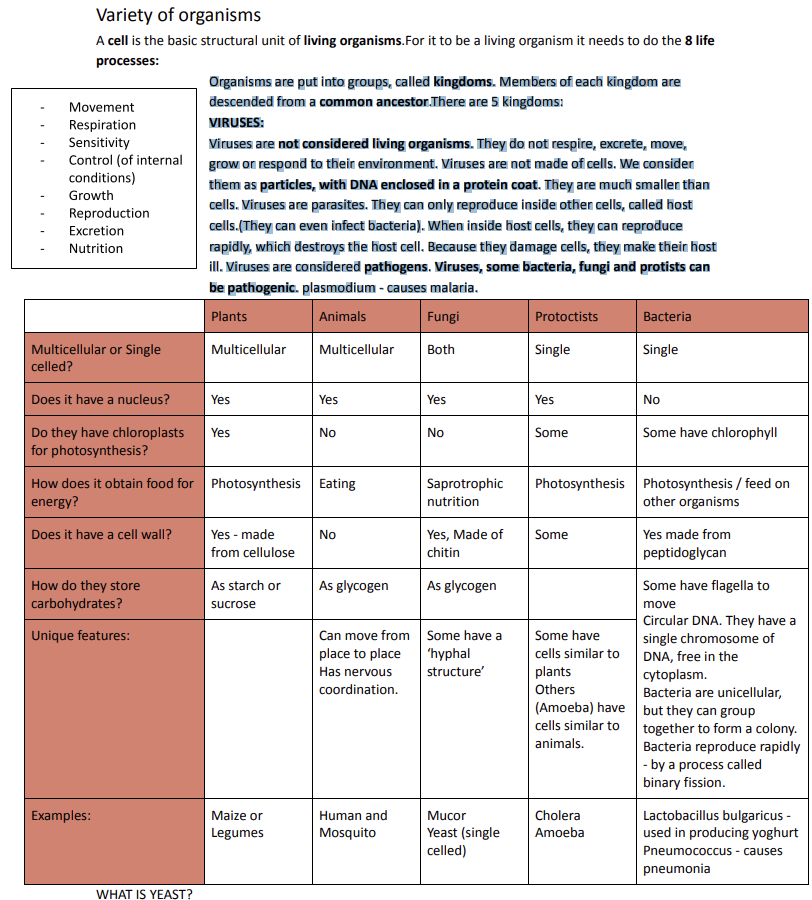
A cell is the basic structural unit of living organisms. For it to be a living organism, it needs to do the 8 life processes:
Organisms are put into groups, called kingdoms. Members of each kingdom are descended from a common ancestor. There are 5 kingdoms:
VIRUSES:
Viruses are not considered living organisms. They do not respire, excrete, move, grow or respond to their environment. Viruses are not made of cells. We consider them as particles, with DNA enclosed in a protein coat. They are much smaller than cells. Viruses are parasites. They can only reproduce inside other cells, called host cells (They can even infect bacteria). When inside host cells, they can reproduce rapidly, which destroys the host cell.

Reviews