IGCSE Biology Ecology Revision Notes
Summary:
The text discusses various concepts related to ecology. It defines key ecological terms like habitat, population, community, and ecosystem. Biodiversity and its significance in maintaining stable ecosystems are highlighted, along with factors that can reduce biodiversity, such as deforestation, global warming, and pollution. The text then explores biotic and abiotic factors that affect ecosystems, including food availability, disease, competition, temperature, light, soil pH changes, and toxic chemicals’ impact.
Sampling methods for estimating population size and biomass are explained, emphasizing random and systematic sampling techniques. The text delves into food chains, food webs, and pyramids of numbers, biomass, and energy in ecosystems. It touches upon the carbon and nitrogen cycles and their importance in nature. Additionally, the text discusses the greenhouse effect, global warming, and its impacts on habitats, food chains, and crop growth. Human contributions to global warming, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, are mentioned.
Furthermore, the text addresses the effects of deforestation, including changes in atmospheric gases and soil quality, as well as the reduction of transpiration and its consequences. Various pollutants like carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide and their negative effects on human health and the environment are discussed. Lastly, the text explains the impact of sewage and pollution by fertilizers, leading to eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems.
Excerpt:
IGCSE Biology Ecology Revision Notes
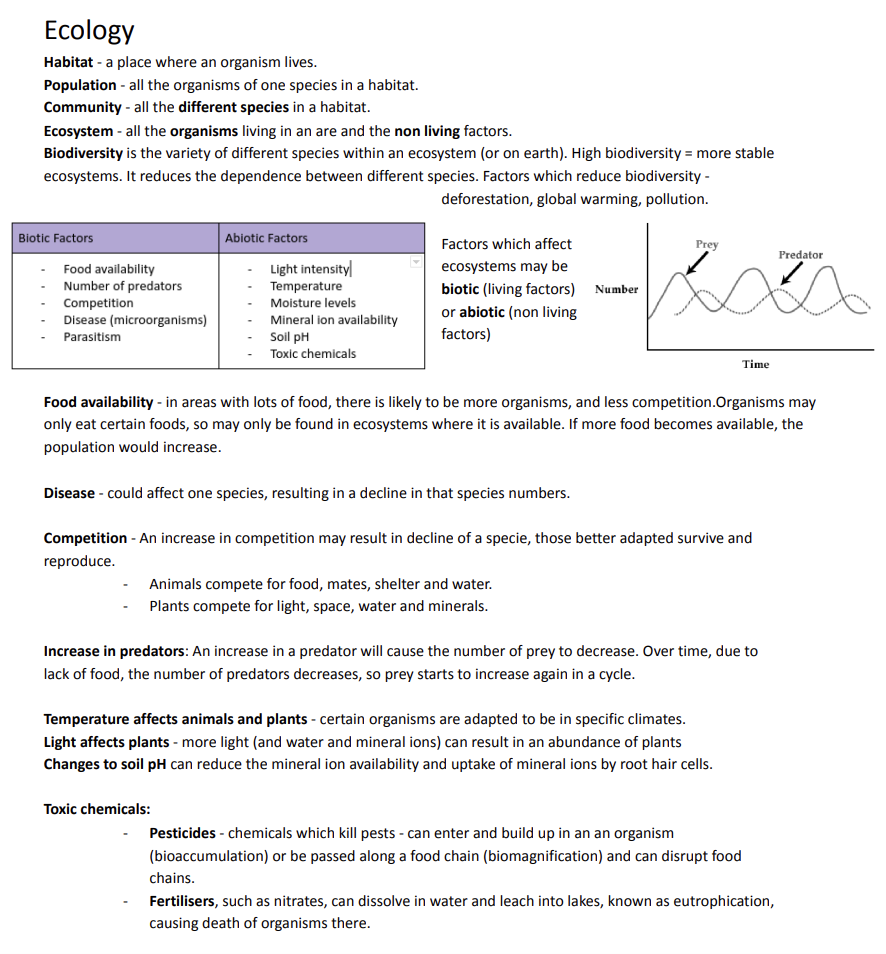
Ecology
– Habitat – a place where an organism lives.
– Population – all the organisms of one species in a habitat.
– Community – all the different species in a habitat.
– Ecosystem – all the organisms living in an area and the non-living factors.
– Biodiversity is the variety of different species within an ecosystem (or on earth). High biodiversity = more stable
ecosystems. It reduces the dependence between different species. Factors that reduce biodiversity – deforestation, global warming, and pollution.
Factors which affect ecosystems may be biotic (living factors) or abiotic (non-living factors).
Food availability – in areas with lots of food, there is likely to be more organisms and less competition. Organisms may only eat certain foods, so may only be found in ecosystems where it is available. If more food becomes available, the population will increase.

Reviews