IGCSE Biology Digestive System
Summary:
The digestive system breaks down food into smaller, soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the blood. It involves both mechanical and chemical processes. Mechanical digestion occurs in the mouth through chewing, while chemical digestion begins with the amylase secretion in the salivary glands to break down starch. The food then travels through the esophagus to the stomach, undergoing further mechanical digestion and chemical digestion of proteins catalyzed by pepsin. The liver produces bile, stored in the gallbladder, to aid in lipid breakdown, while the pancreas further releases digestive enzymes to digest food in the small intestines.
In the small intestines, the final digestion takes place, and the products of digestion are absorbed into the blood. The duodenum, jejunum, and ileum are parts of the small intestines, and it is in the ileum where absorption occurs. Bile plays a crucial role in neutralizing the acidic contents from the stomach and emulsifying fats to increase their surface area for easier breakdown. The absorbed products of digestion are transported around the body to be utilized or stored. The small intestines’ lining contains villi and microvilli, which provide a large surface area for absorption. Villi have only one cell thick walls, allowing for efficient diffusion of nutrients into the blood.
Muscles in the gut, specifically circular and longitudinal muscles, move food along the digestive tract through peristalsis. The absorption process involves active transport, facilitated diffusion, and simple diffusion of nutrients into the blood. The lacteal in each villus carries products of fat digestion, transporting them into the lymph and eventually draining into the blood.
Excerpt:
IGCSE Biology Digestive System
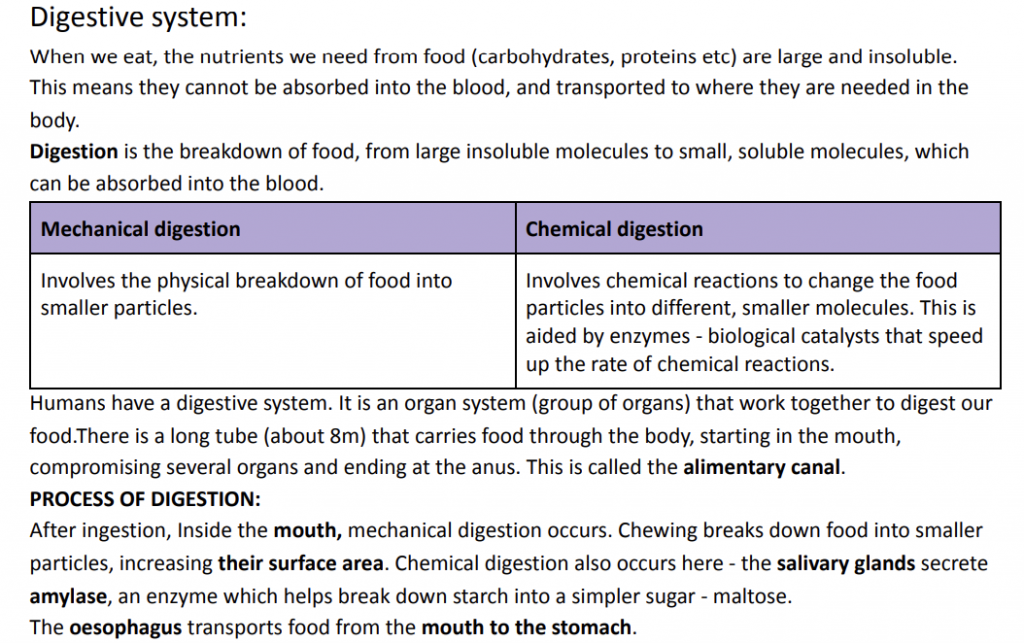
Digestive system:
When we eat, the nutrients we need from food (carbohydrates, proteins etc) are large and insoluble. This means they cannot be absorbed into the blood, and transported to where they are needed in the body.
Digestion is the breakdown of food, from large insoluble molecules to small soluble molecules, which can be absorbed into the blood.

Reviews