Human Biology on Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses – ATAR Year 12
Summary:
This passage discusses nerve cells and nerve impulses. Nerve cells, also known as neurons, consist of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. The myelin sheath, produced by Schwann cells, protects and insulates the axon, speeding up the transmission of nerve impulses. There are different types of neurons, including sensory neurons, interneurons/relay neurons, and motor neurons, each with its own function. Synapses are junctions or gaps between adjacent neurons where nerve impulses are transmitted. Nerve impulses are electrochemical changes that travel along nerve fibers and involve a change in electrical voltage due to ion concentration changes. The generation of an action potential involves depolarization and repolarization of the cell membrane. Nerve impulses can be transmitted through continuous propagation along unmyelinated fibers or saltatory conduction along myelinated fibers. Synaptic transmission occurs when an action potential reaches the axon terminal, leading to the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. Chemicals can have various effects on synaptic transmissions, such as stimulating or depressing the transmission.
Excerpt:
Human Biology on Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
…
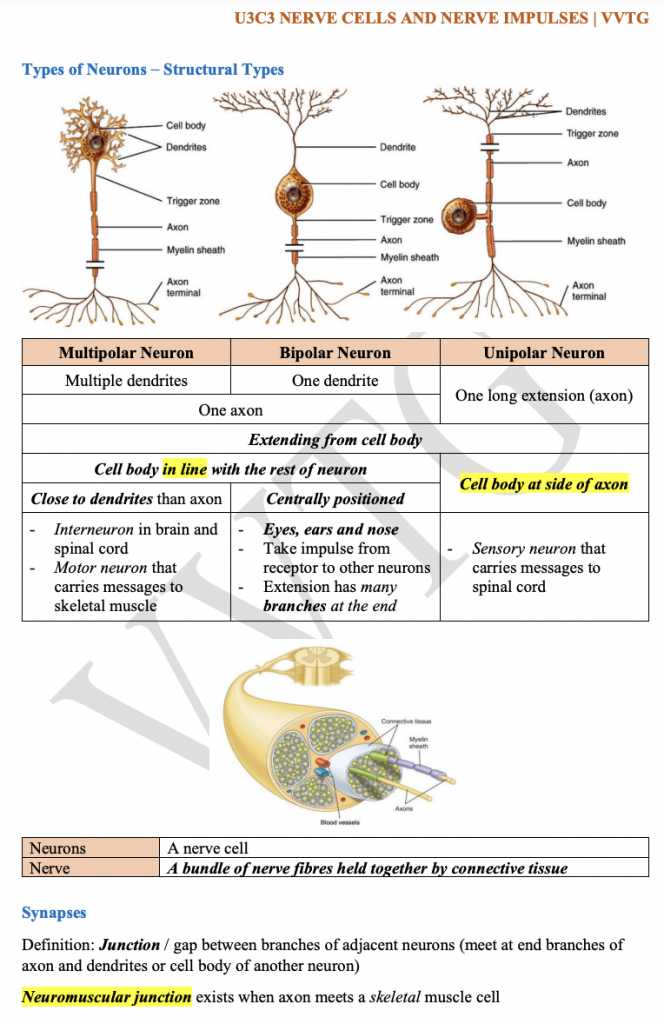
Nerve Cells / Neurons consist of:
- Cell body: Cytoplasm contains a nucleus and other organelles
- Dendrites: Short extension from the cell body
- Axon/Nerve fibers: Long extension from the cytoplasm
Myelinated Fibres
- Myelin sheath is produced by special Schwann cells, which wrap around the axon
- An outermost coil of the Schwann cell forms a neurilemma, which helps in the repair of injured fibers
- Intervals along the axon are gaps in the myelin sheath, called nodes of Ranvier
- In the brain and spinal cord, the myelin sheath is produced by oligodendrocytes
Roles of Myelin Sheath
- Protects nerve fiber from damage
- Insulates axons
- Speeds up the transmission of nerve impulse
Types of Neurons
- Functional Types
- Sensory Neurone: Carry messages from receptors to CNS
- Interneuron/Relay Neurone: Located in CNS and link between sensory and motor neurons
- Motor Neurone: Carry messages from CNS to effectors

Reviews