Human Biology Divisions of The Nervous System – ATAR YEAR 12
Summary:
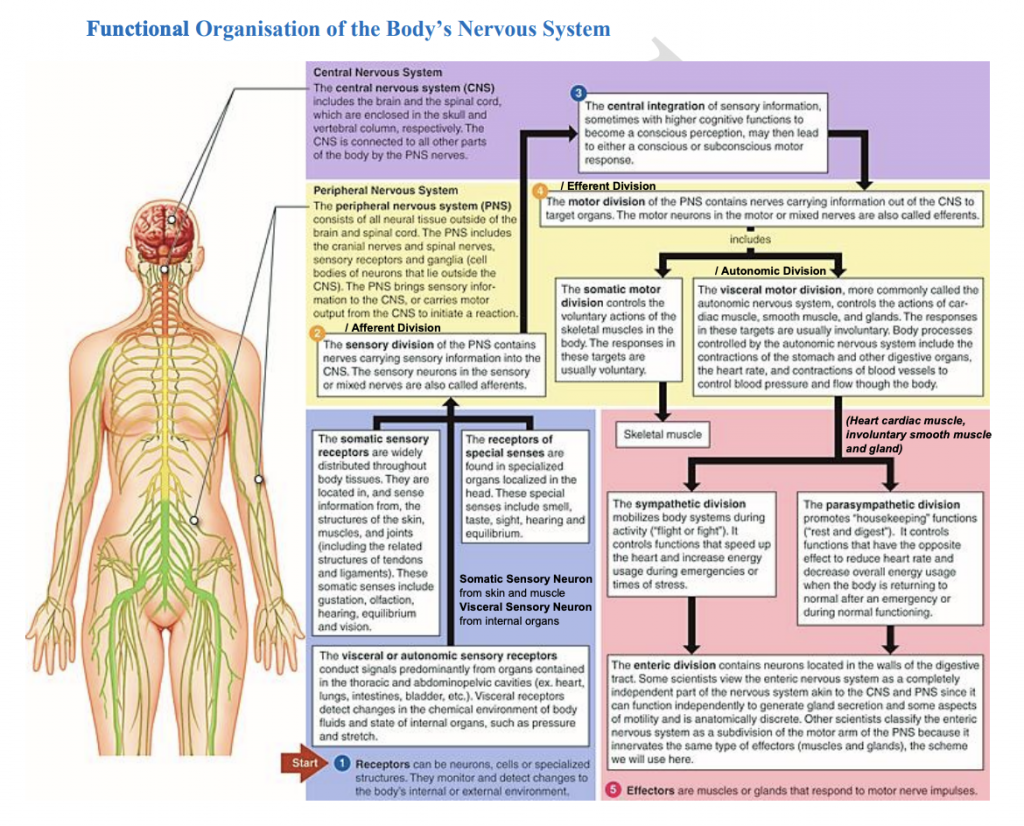
The nervous system can be divided into different functional parts. Ganglia are groups of nerve cell bodies located outside the central nervous system (CNS). The peripheral nervous system includes cranial nerves and spinal nerves, which transmit sensory and motor impulses between the body and the CNS. The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions and operates without conscious control. It is controlled by nerve cell groups in the medulla oblongata, hypothalamus, and cerebral cortex.
There are differences between the somatic and autonomic divisions of the peripheral nervous system. The somatic division responds to the external environment and is usually under voluntary control, while the autonomic division maintains homeostasis and operates involuntarily. The autonomic division consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, which have different effects on target organs. The sympathetic system releases noradrenaline, leading to excitation, while the parasympathetic system releases acetylcholine, causing excitation or inhibition.
The autonomic nervous system plays a role in the fight-or-flight response. In threatening situations involving fear, anger, stress, danger, or competition, sympathetic stimulation dominates, leading to increased activity. Various bodily structures and functions are affected, such as dilated pupils, increased heart rate, dilated airways, vasoconstriction in blood vessels, increased blood glucose levels, and the release of adrenaline and noradrenaline.
The coordination between the nervous and endocrine systems has similarities and differences. Some hormones are secreted by neurons, and some substances function as both hormones and neurotransmitters. Both systems can have similar effects on target cells. However, hormonal coordination involves transport through the bloodstream, resulting in slower and longer-lasting responses compared to the rapid and localized responses of nervous coordination.
Overall, the divisions of the nervous system and their coordination with other systems play crucial roles in maintaining bodily functions and responding to internal and external stimuli.
Excerpt:
Human Biology Divisions of The Nervous System
U3C4 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM | VVTG
Subtopic Content
4.1 Divisions of the Nervous System
4.2 The Autonomic Nervous System Fight-or-Flight Response
4.3 Comparison of Hormonal and Nervous Coordination

Reviews