Homeostasis Year 10 Notes (Grade A+)
Summary:
Homeostasis (Grade A+)
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment necessary for healthy functioning. Negative feedback control is used to regulate blood sugar concentration, water concentration, and temperature of the blood. The process involves a stimulus, a receptor that detects the stimulus, and a self-regulatory corrective mechanism. Organs involved in homeostasis include the skin for temperature regulation, the kidneys for water concentration, the brain, and the pancreas for producing insulin to control blood sugar concentration.
Excerpt:
Homeostasis
- Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of a constant internal environment.
- Need for Homeostasis
- Changes in body temperature may result in enzyme inactivation or denaturation.
- Any drastic changes in our blood and the surrounding tissues’ fluid will affect chemical reactions in the tissue cells and will harm the body.
- Cells must be bathed in tissue fluid of the correct pH and water potential. Enzyme reaction will be affected.
Negative Feedback Control
- The internal environment of our bodies MUST have certain conditions within tolerable limits to continue healthy functioning.
- Done by NEGATIVE FEEDBACK control.
- Used to control blood sugar concentration, water concentration & temperature of the blood.
- Negative Feedback
- A stimulus, which is the change in the internal environment
- A receptor that can detect the stimulus
- A self-regulatory corrective mechanism
- Negative feedback to the receptor
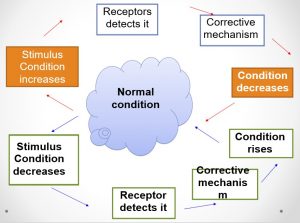
Homeostasis
Organs Involved in Homeostasis
- Skin – helps in temperature regulation
- Kidneys – help in the water concentration of the body
- Brain
- Pancreas – produces insulin that helps in the control of sugar concentration in the blood
Examples of Homeostasis
Regulation of blood glucose concentration
Too much glucose in the blood
- Stimulate the pancreas to secrete more insulin
- Causes the liver to convert glucose to glycogen
- Blood glucose level drops
- Achieved normal blood glucose level
Too little glucose in the blood
- Stimulate the pancreas to secrete glucagon which causes the liver to convert glycogen to glucose
- Blood glucose level rises
- Achieved normal blood glucose level


Reviews