Guide to Engineering Graphics and Design (Grade A)
Summary:
The Guide to Engineering Graphics and Design provides a comprehensive overview of Engineering Graphics & Design (EGD), a crucial area of study for engineering. It starts with the concept of scales, detailing various types, uses, and related problems. It then explores engineering curves, breaking them down into conic sections (Ellipse, Parabola, Hyperbola), involutes, cycloids, trochoids, and spirals. The note further delves into the loci of points, highlighting the definitions, classifications, and basic locus cases.
The fundamentals of Orthographic Projections are covered, explaining types, planes, and methods of orthographic projections, as well as the conversion of pictorial views into orthographic views. It also thoroughly explores projections of points and lines, discussing the structure of quadrants, projections in different quadrants, lines inclined to planes, and traces of lines.
The note concludes with the lines’ applications, offering various problems for practice. With its systematic approach to EGD topics, the note provides an essential resource for mastering the subject.
Excerpt:
Guide to Engineering Graphics and Design
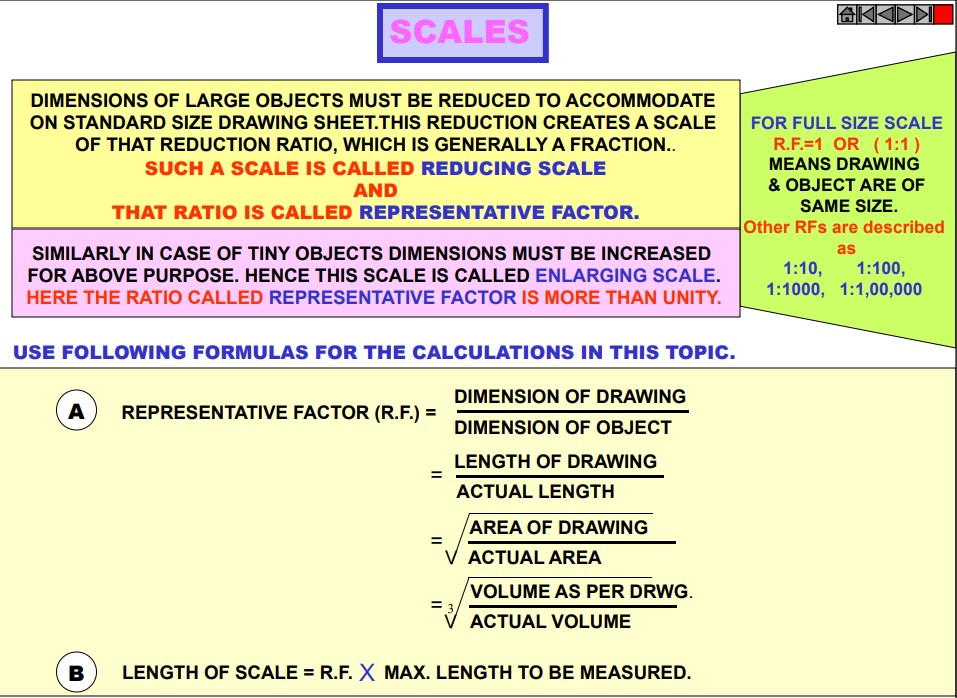
Scales
1. Basic Information
2. Types and important units
3. Plain Scales (3 Problems)
4. Diagonal Scales – information
5. Diagonal Scales (3 Problems)
6. Comparative Scales (3 Problems)
7. Vernier Scales – information
8. Vernier Scales (2 Problems)
9. Scales of Cords – construction
10. Scales of Cords (2 Problems)
Engineering Curves – I
1. Classification
2. Conic sections – explanation
3. Common Definition
4. Ellipse – ( six methods of construction)
5. Parabola – ( Three methods of construction)
6. Hyperbola – ( Three methods of construction )
7. Methods of drawing Tangents & Normals ( four cases)
Engineering Curves – II
1. Classification
2. Definitions
3. Involutes – (five cases)
4. Cycloid
5. Trochoids – (Superior and Inferior)
6. Epic cycloid and Hypo – cycloid
7. Spiral (Two cases)
8. Helix – on cylinder & on cone
9. Methods of drawing Tangents and Normals (Three cases)
Loci of Points
1. Definitions – Classifications
2. Basic locus cases (six problems)
3. Oscillating links (two problems)
4. Rotating Links (two problems)
Orthographic Projections – Basics
1. Drawing – The fact about
2. Drawings – Types
3. Orthographic (Definitions and Important terms)
4. Planes – Classifications
5. Pattern of planes & views
6. Methods of orthographic projections
7. 1st angle and 3rd angle method – two illustrations

Reviews