FINC2011 Corporate Finance Notes
Summary:
The summary covers the complete content of the course during the semester, focusing on various aspects of finance and financial markets. It begins with an introduction to finance and financial markets, providing an overview of the modern financial system. The note includes a section on financial mathematics, likely covering essential mathematical concepts relevant to finance.
The topics covered also encompass the valuation of stocks and bonds and capital budgeting, which is likely divided into two parts (Capital Budgeting – I and Capital Budgeting – II). The concepts of risk and return are explored, and the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is likely discussed as a tool for determining the expected return on an investment based on its risk.
The note delves into the company’s cost of capital, which is crucial for making financial decisions. Equity capital markets are covered, and the efficiency of asset markets and the influence of behavioural finance are likely addressed.
Finally, the note includes a section on business ethics, which is significant for understanding the ethical implications and considerations in financial decision-making.
The content is supplemented with lecture slides and a textbook, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the course material throughout the semester.
Excerpt:
FINC2011 Corporate Finance Notes
INTRODUCTION TO FINANCE AND FINANCIAL MARKETS
WHAT IS FINANCE?
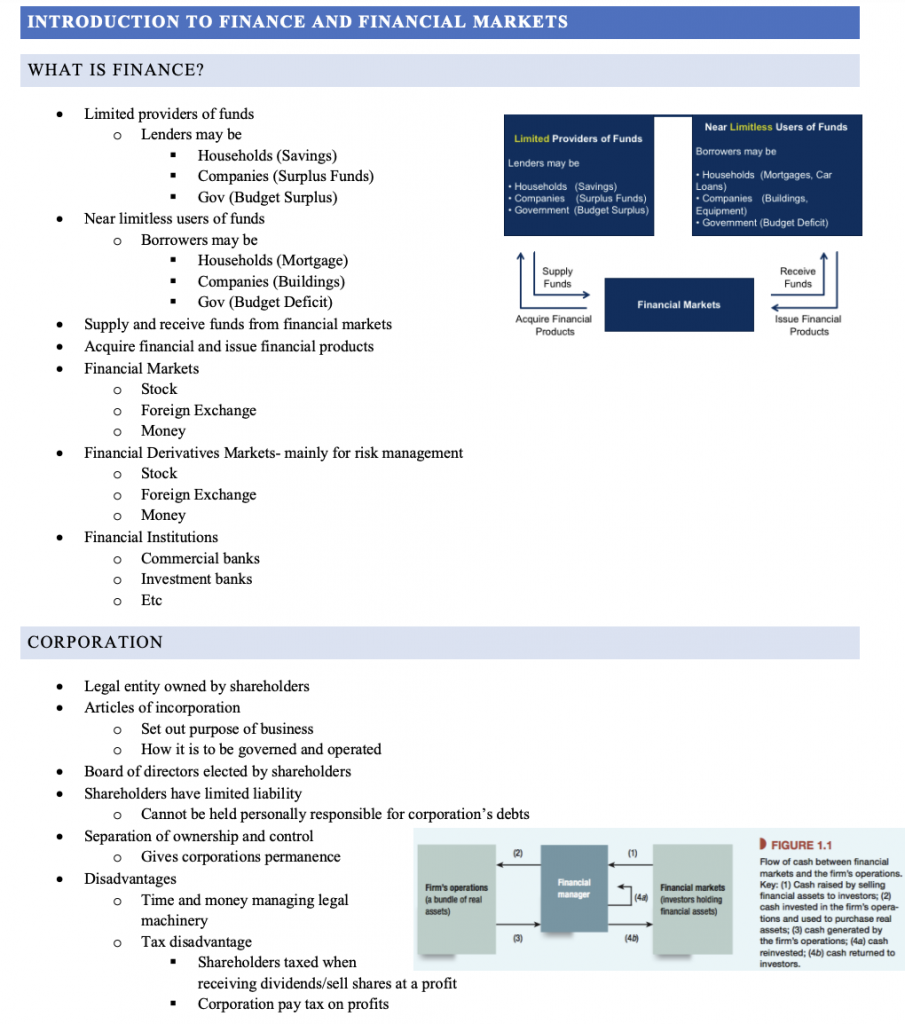
- Limited providers of funds
- Lenders may be
- Households (Savings)
- Companies (Surplus Funds)
- Gov (Budget Surplus)
- Lenders may be
- Near limitless users of funds
- Borrowers may be
- Households (Mortgage)
- Companies (Buildings)
- Gov (Budget Deficit)
- Borrowers may be
- Supply and receive funds from financial markets
- Acquire financial and issue financial products
- Financial Markets
- Stock
- Foreign Exchange
- Money
- Financial Derivatives Markets – mainly for risk management
- Stock
- Foreign Exchange
- Money
- Financial Institutions
- Commercial banks
- Investment banks
- Etc
CORPORATION
- A legal entity owned by shareholders
- Articles of incorporation
- Set out the purpose of business
- How it is to be governed and operated
- Board of Directors elected by shareholders
- Shareholders have limited liability
- Cannot be held personally responsible for corporation’s debts
- Separation of ownership and control
- Gives corporations permanence
- Disadvantages
- Time and money managing legal machinery
- Tax disadvantage
- Shareholders are taxed when receiving dividends/sell shares at a profit
- Corporations pay tax on profits

Reviews