Exploring Hyperkalemia
Summary:
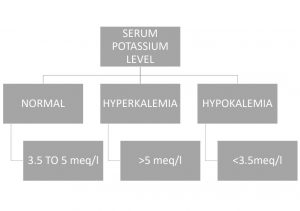
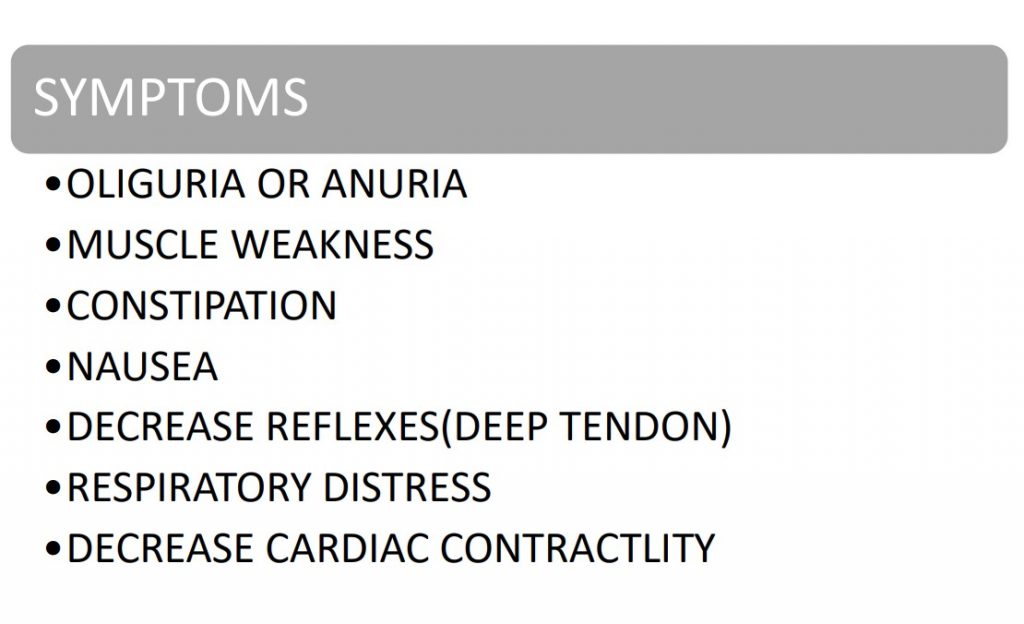
Hyperkalemia is a condition characterized by abnormally high serum potassium levels (>5 meq/l), while hypokalemia refers to abnormally low levels (<3.5 meq/l). Various factors can contribute to hyperkalemia, including decreased potassium excretion (e.g., kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, decreased aldosterone), transcellular shift (e.g., diabetes mellitus, dehydration, certain medications), and increased intake (e.g., potassium supplements, certain foods). Symptoms of hyperkalemia include muscle weakness, constipation, nausea, decreased reflexes, respiratory distress, and decreased cardiac contractility.
Diagnosing hyperkalemia involves assessing potassium excretion (aldosterone levels, urine output), intake history (medications), and identifying signs such as increased blood glucose, creatine kinase, myoglobin in urine, and abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG) findings. Treatment aims to address the underlying cause and includes strategies to decrease potassium excretion (diuretics, dialysis), promote transcellular shift (insulin, dextrose, bicarbonate), and manage potassium intake.
Pseudohyperkalemia is a phenomenon where serum potassium levels appear falsely elevated due to disruption of cells during sample collection or processing.
Excerpt:
Exploring Hyperkalemia
Exploring Hyperkalemia Image
CAUSES
DECREASE EXCRETION
• ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
• SEVERE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
• DECREASE ALDOSTERONE
• POTASSIUM-SPARING DIURETICS
• NON-STEROIDAL ANTIINFLAMMATORY DRUGS
• ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING
ENZYME BLOCKERS
• ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS
TRANSCELLULAR SHIFT
• DIABETES MELLITUS TYPE-1 OR TYPE-2
• SEVERE DEHYDRATION
• DIGOXIN
• INCREASE DIURESIS
• RHABDOMYOLYSIS
• RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS
• BETA-BLOCKERS
• HAEMOLYSIS
• TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME
INCREASE INTAKE
• MEDICATION FOR HYPOKALEMIA• FOOD
SYMPTOMS
•OLIGURIA OR ANURIA
•MUSCLE WEAKNESS
•CONSTIPATION
•NAUSEA
•DECREASE REFLEXES(DEEP TENDON)
•RESPIRATORY DISTRESS
•DECREASE CARDIAC CONTRACTILITY
DIAGNOSIS
DECREASE EXCRETION
• DECREASE ALDOSTERONE
• DECREASE URINE OUTPUT
• INCREASE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE
• INCREASE CREATININE
• INCREASE RENIN
• INCREASE BLOOD UREA NITROGEN
INCREASE INTAKE
• HISTORY OF MEDICATIONS THAT INCREASE POTASSIUM LEVEL
• POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETICS• NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS
• ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME BLOCKERS
• ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS• DIGOXIN
• BETA-BLOCKERS
DIAGNOSIS – TRANSCELLULAR SHIFT
• INCREASE BLOOD GLUCOSE
• INCREASE CREATINE KINASE • INCREASE MYOGLOBIN IN URINE
• INCREASE PHOSPHATE
• INCREASE URIC ACID
• ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
• PEAKED T WAVE
• WIDE QRS COMPLEX
• PROLONGED PR INTERVAL
• FLAT OR ABSENT P WAVE
• SINE WAVE • VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION • ASYSTOLE
• ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS ANALYSIS• INCREASE CARBON DIOXIDE• DECREASE PH• DECREASE BICARBONATE• CBC
• INCREASE RED BLOOD CELLS• INCREASE PLATELETS
• INCREASE LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE• INCREASE UNCONJUGATED BILIRUBIN• DECREASE FREE HAPTOGLOBIN

Reviews