Economics for Business Notes
Summary:
Lecture 1 covers fundamental economic concepts. People make trade-offs, and costs include monetary and opportunity costs. Rational decisions are made at the margin, considering marginal cost and marginal benefit. People respond to incentives that influence decisions. The supply and demand model defines competitive markets. Demand depends on price, following the law of demand. Changes in demand include income, price of related goods, taste, expectations, and number of buyers. Supply depends on price, following the law of supply. Input prices, technology, expectations, and the number of sellers influence changes in supply. Equilibrium occurs when supply and demand balance, determining equilibrium price and quantity. Elasticity measures responsiveness to changes in determinants. Price elasticity of demand, cross-price elasticity, and determinants of price elasticity of supply are discussed.
Excerpt:
Economics for Business Notes
Lecture 1

Economics for Business Notes

Economics for Business Notes

Economics for Business Notes
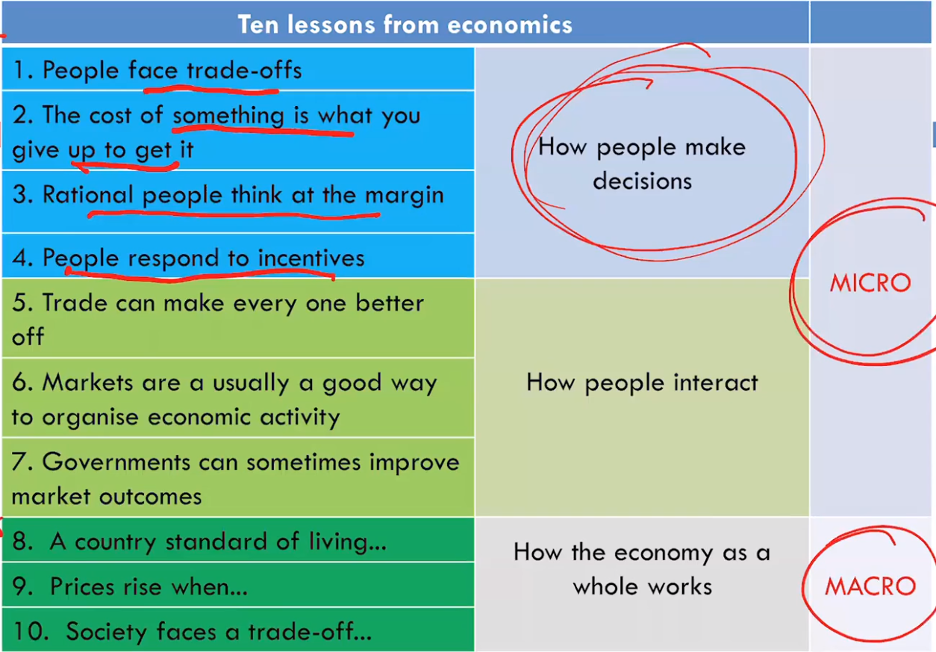
| 1. People face trade-offs | – Giving one goal to achieve another |
| 2. The cost of something is what you give to get it | – Refers to monetary costs and opportunity costs
– The cost of an item/service/ activity in comparison to the monetary value of what you’re giving up cost and benefits of the decision
– Opportunity cost: the next best alternative that you give up to obtain that item (e.g. giving up games for school)
|
| 3. Rational People think at the margin | – Marginal change: small incremental changes to a given plan of action
● Marginal Cost (MC): cost associated ● Marginal Benefit (MB: benefit associated
|
| 4. People respond to incentives | – Incentive: reward or punishment that induces a person to act in a certain way
– Incentives affect the benefits and cost of decisions (e.g. government policies consist of large sets of incentives to encourage and discourage. |
| Supply and Demand | ● Economists introduce a model of a market for goods and services
Market and Competition ● Market: a group of buyers and sellers of goods/services ● Competitive Market: so many buyers and sellers that have a negligible impact on the market price ● Market is perfectly competitive (PC). This includes aspects:
|

Reviews