Economic Theory Applied
Summary:
“Economic Theory Applied Notes” provides a comprehensive understanding of key concepts in macroeconomics, including living standards, aggregate demand and supply, and macroeconomic goals.
It highlights the difference between Material and Non-Material Living Standards. Material Living Standards measure the economic well-being of individuals through the number of physical goods and services they can consume. Non-Material Living Standards, on the other hand, consider the quality aspects of a person’s daily life, including happiness, physical and mental health, social relationships, and societal factors like the absence of crime and justice.
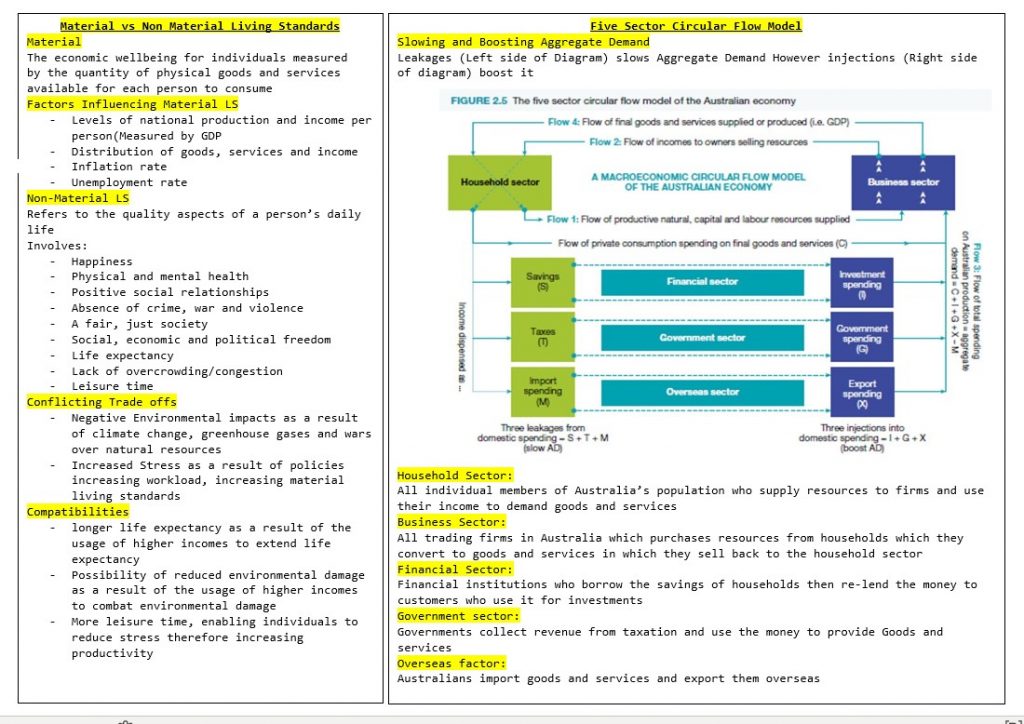
The Five Sector Circular Flow Model is explained, which includes the household, business, financial, government, and overseas sectors. These all interact in a complex system that influences aggregate demand and supply.
The note covers the concepts of aggregate demand and supply extensively, detailing their compositions, influences, and effects on economic conditions. Aggregate Demand and Supply are crucial elements representing the total demand for and supply of goods and services within an economy at a given overall price and time.
Three core Macroeconomic Goals are examined: Full Employment, Strong and Sustainable Economic Growth, and Low Inflation. Full Employment aims to maintain an unemployment rate that balances low inflation and other economic goals. It’s also explained why a 0% unemployment rate is undesirable, often leading to excessive aggregate demand, capacity constraints, and inflationary pressure.
Excerpt:
Economic Theory Applied
Material vs Non-Material Living Standards
Material
The economic well-being of individuals measured
by the number of physical goods and services
available for each person to consume
Factors Influencing Material LS
- Levels of national production and income per person(Measured by GDP
- Distribution of goods, services and income
- Inflation rate
- Unemployment rate
Non-Material LS
Refers to the quality aspects of a person’s daily life
Involves:
- Happiness
- Physical and mental health
- Positive social relationships
- Absence of crime, war and violence
- A fair, just society
- Social, economic and political freedom
- Life expectancy
- Lack of overcrowding/congestion
- Leisure time
Conflicting Trade-offs
- Negative Environmental impacts as a result of climate change, greenhouse gases and wars over natural resources
- Increased Stress as a result of policies increasing workload, increasing material living standards

Reviews