Drugs Table of Cardiovascular Pharmacology (Grade A+)
Summary:
Drugs Table of Cardiovascular Pharmacology
11 Drugs Used in Hypertension 101
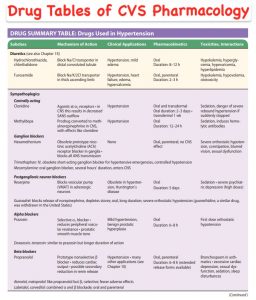
This chapter provides a summary of drugs commonly used to treat hypertension. The drug summary table offers an overview of different subclasses, including diuretics, sympathoplegics, ganglion blockers, postganglionic neuron blockers, alpha-blockers, beta-blockers, vasodilators, renin antagonists, and angiotensin antagonists.
Diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone work by blocking the Na/Cl transporter in the distal convoluted tubule, and are used for hypertension and mild edema. Furosemide, another diuretic, blocks the Na/K/2Cl transporter in the thick ascending limb and is indicated for hypertension, heart failure, edema, and hypercalcemia.
Sympathoplegics like clonidine and methyldopa act centrally to decrease sympathetic outflow, while ganglion blockers such as hexamethonium and trimethaphan block the transmission of signals in the autonomic nervous system.
Postganglionic neuron blockers like reserpine and guanadrel interfere with adrenergic neuron function, and alpha-blockers like prazosin reduce peripheral vascular smooth muscle tone. Beta-blockers, such as propranolol, reduce renin release and are used for various applications, including angina and hypertension.
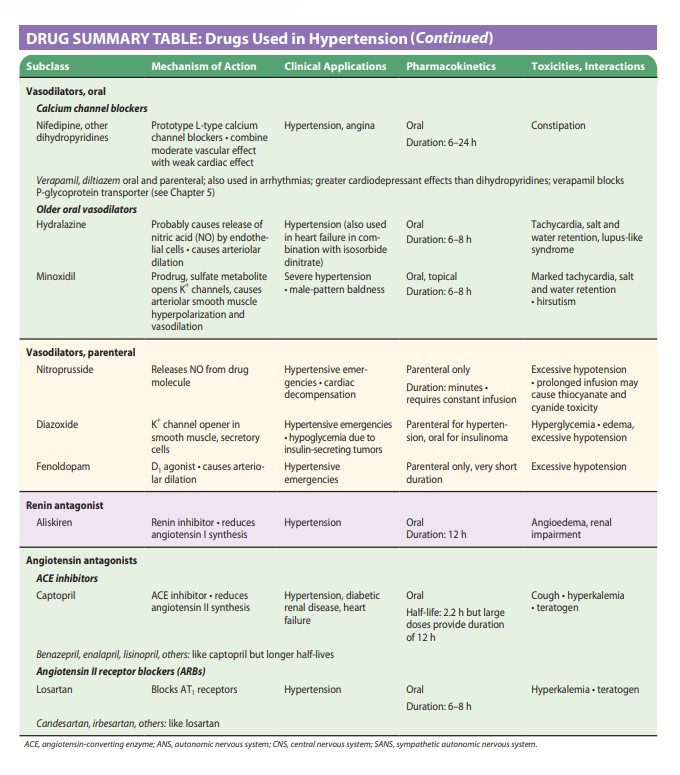
Vasodilators include calcium channel blockers like nifedipine and verapamil, as well as older oral vasodilators like hydralazine and minoxidil. These drugs have different mechanisms of action and are used for conditions such as hypertension, angina, and heart failure.
Renin antagonists like aliskiren and angiotensin antagonists (ACE inhibitors and ARBs) such as captopril and losartan target the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to control blood pressure and treat conditions like hypertension, diabetic renal disease, and heart failure.
The chapter also briefly covers drugs used to treat angina pectoris and arrhythmias. Antianginal drugs like nitroglycerin and calcium channel blockers, as well as antiarrhythmic drugs classified into four groups (I-IV), are mentioned.
Overall, this drug summary table provides a concise overview of various drug classes used in the management of hypertension, angina, and related cardiovascular conditions, aiding in understanding their mechanisms of action, clinical applications, pharmacokinetics, and potential toxicities.
Excerpt:
Drugs Table of Cardiovascular Pharmacology
DRUG SUMMARY TABLE: Drugs Used in Hypertension
Drug Tables of CVS Pharmacology

Reviews