Complete Notes for Psychology Units 3/4
Summary:
This text summarises psychology notes on the nervous system, specifically focusing on the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), including its divisions: somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The CNS, consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives sensory information and controls voluntary and involuntary bodily functions. The PNS transfers sensory and motor messages between the CNS and the rest of the body. The autonomic nervous system, a subdivision of the PNS, regulates involuntary functions, such as heart rate and breathing, through its sympathetic and parasympathetic branches. Conscious and unconscious responses to sensory stimuli are discussed, with reflex actions being an example of unconscious responses that bypass the brain to allow for rapid reactions to potential dangers. Biofeedback, yoga, and meditation can help control autonomic physiological activity.
Excerpt:
Complete Notes for Psychology Units 3/4
Unit three
HOW DOES EXPERIENCE AFFECT BEHAVIOUR AND MENTAL PROCESSES?
Area of study 1
HOW DOES THE NERVOUS SYSTEM ENABLE PSYCHOLOGICAL FUNCTIONING?
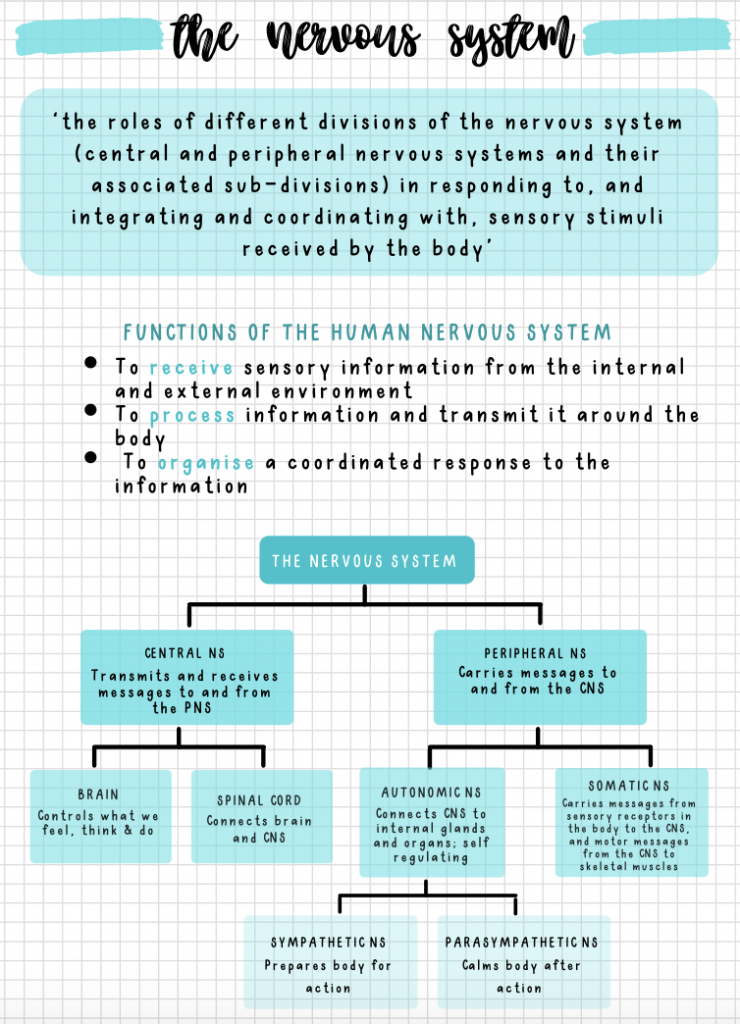
The nervous system:
- To receive sensory information from the internal and external environment
- To process information and transmit it around the body
- To organize a coordinated response to the information
- The roles of different divisions of the nervous system (central and peripheral nervous systems and their associated sub-divisions) in responding to, integrating and coordinating with, sensory stimuli received by the body
Functions of the Human Nervous System:
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM:
CENTRAL NS: Transmits and receives messages to and from the PNS
PERIPHERAL NS: Carries messages to and from the CNS
SOMATIC NS: Carries messages from sensory receptors in the body to the CNS, and motor messages from the CNS to skeletal muscles
AUTONOMIC NS: Connects CNS to internal glands and organs; self-regulating
BRAIN:
- Controls what we feel, think & do
- The brain is a complex structure that consists of +/- 100 billion neurons
- It contains more than 90 per cent of the central nervous system’s neurons
- The brain is responsible for how we think and feel, how we perceive the world and constructing a sense of who we are
- The brain communicates with the rest of the brain through the spinal cord

Reviews