Class 10 Math on Understanding Triangles
Summary:
This mathematics formula guide for Class 10 focuses on triangles, which are three-sided closed figures. Triangles can be classified based on sides (scalene with no equal sides, isosceles with two equal sides, and equilateral with all sides equal) or angles (acute with all angles acute, right-angled with one right angle, and obtuse-angled with one obtuse angle). The concept of triangle similarity, where triangles have the same shape but not necessarily the same size, is introduced, with similarity based on equal corresponding angles and proportional corresponding sides. The Basic Proportionality Theorem (Thales Theorem) and its converse relate to lines intersecting or dividing the triangle’s sides. The AAA and SSS rules define the criteria for triangle similarity. Key triangle formulas include the area (A = 1/2 × base × height) and the perimeter (P = sum of the sides). Class 10 also covers triangle and circle theorems like Pythagoras’ Theorem, Midpoint Theorem, Angle Bisector Theorem, and others. The area of a triangle encompasses the entire region within its three sides. Congruency rules are also mentioned, including SSS, SAS, ASA, and AAS.
Excerpt:
Maths Formulas For Class 10 Chapter- Triangles Formula
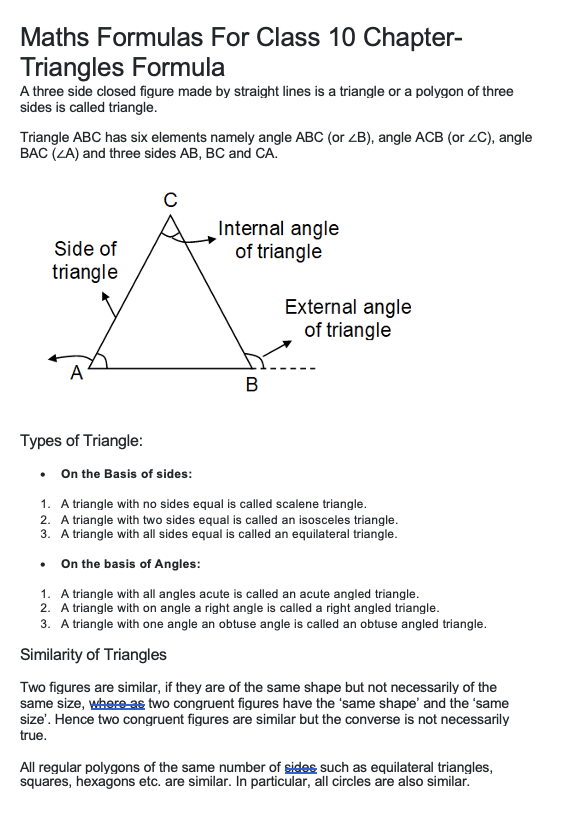
A three side closed figure made by straight lines is a triangle, or a polygon of three sides is called a triangle.
Triangle ABC has six elements, namely angle ABC (or ∠B), angle ACB (or ∠C), angle BAC (∠A) and three sides AB, BC and CA.
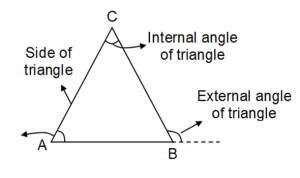
Class 10 Math on Understanding Triangles
Types of Triangle:
- Based on sides:
- A triangle with no equal sides is called a scalene triangle.
- A triangle with two sides equal is called an isosceles triangle.
- A triangle with all sides equal is called an equilateral triangle.
- On the basis of Angles:
- A triangle with all acute angles is called an acute-angled triangle.
- A triangle with one angle and a right angle is called a right-angled triangle.
- A triangle with one angle, an obtuse angle, is called an obtuse angled triangle.

Reviews