Chemistry in Everyday Life
Summary:
Chemistry is crucial in everyday life, especially medicine, food, and cleansing agents. Drugs, which interact with macromolecules to produce a biological response, can be therapeutic medicines or become poisons if misused. They are classified based on pharmacological effects, drug action on biochemical processes, chemical structure, and molecular targets. Enzymes and receptors are common drug targets, with enzyme inhibitors blocking enzyme functions, while agonists mimic natural messengers to activate receptors. In food, chemicals like artificial sweeteners, preservatives, and antioxidants enhance preservation, flavour, and nutritional value. Soaps and synthetic detergents aid in cleansing, with detergents offering advantages in hard water due to their ability to form foam in various conditions. However, properly managing detergent composition is essential to prevent pollution caused by their slow degradation.
Excerpt:
Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chemistry has been used for the benefit of mankind. It includes medicines, food materials, cleansing agents etc.
1. DRUGS AND THEIR CLASSIFICATION
Drugs are chemicals of low molecular masses (~100 – 500u) that interact with macromolecular targets and produce a biological response.
– Medicines are called medicines if the biological response is therapeutic and useful.
– If taken in higher than recommended doses, drugs may become poisons.
– Chemotherapy: Use of chemicals for therapeutic effect.
– Drugs are classified as follows:
(a) based on pharmacological effect:
– It is useful for doctors because it provides drugs to treat a particular problem.
– E.g. analgesics (pain-killing effect), antiseptics (kill or arrest microbial growth).
(b) based on the drug’s action on a biochemical process:
– E.g. Antihistamines inhibit the action of histamine, which causes inflammation in the body.
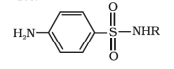
(c) based on the chemical structure of the drug:
– This shows common structural features of drugs. They often have similar pharmacological activity.
– E.g. sulphonamides.
Chemistry in Everyday Life
(d) based on molecular targets:
– This classification is most useful for medicinal chemists.
– Drugs interact with target molecules (drug targets) such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
– Drugs possessing some common structural features may have the same mechanism of action on targets.


Reviews