A complete term’s worth of extensive biology notes regarding the topic of Reproduction. These notes cover, in thorough detail, the following learning intentions: (1) Asexual and sexual reproduction (reproductive process, examples, advantages and disadvantages)
(2) Plant asexual reproduction (vegetative propagation, fragmentations, spore formations, etc.)
(3) Plant sexual reproduction (anatomy and physiology)
(4) Pollination (self-pollination and cross-pollination)
(5) Types of flowers (entomophilous and anemophilous)
(6) Plant fertilisation (single and double fertilisation involving endosperm nucleus)
(7) Seeds and germination (including seed dispersal)
(8) Fruit (structure and function)
(9) Alternation of generations (process of haploid multicellular generation and diploid generation, i.e. distinguishing gametophytes and sporophytes)
(10) Diversity in reproductive strategies (internal and external fertilisation using examples such as planulae and hermaphroditism)
(11) Mitosis and meiosis (only a brief overview, this is typically a ‘refresher’ and is usually learned extensively in the Genetics unit)
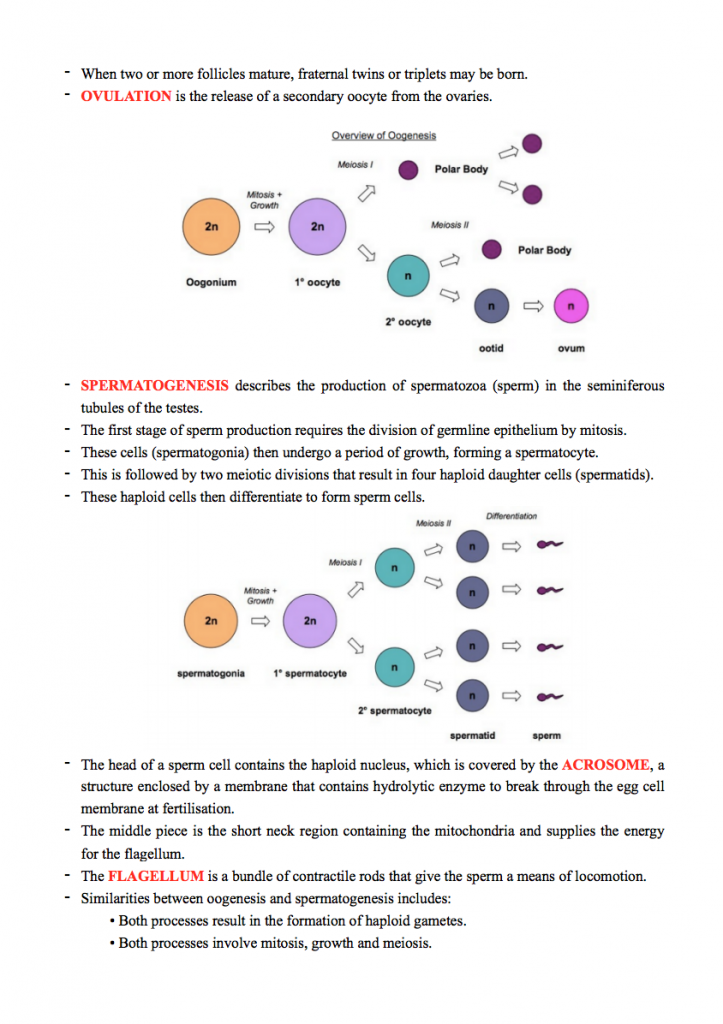
(12) Gametogenesis, oogenesis (polar bodies, secondary oocytes and corpus luteum), spermatogenesis (process)
(13) Structure of the sperm cell (acrosome, flagellum)
(14) Differences between oogenesis and spermatogenesis
(15) Male reproductive system (anatomy and physiology)
(16) Female reproductive system (anatomy and physiology)
(17) Menstrual cycle (thorough explanation of entire process involving follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinising hormone and the role of oestrogen and progesterone)
(18) Pheromones, ectohormones and testosterone
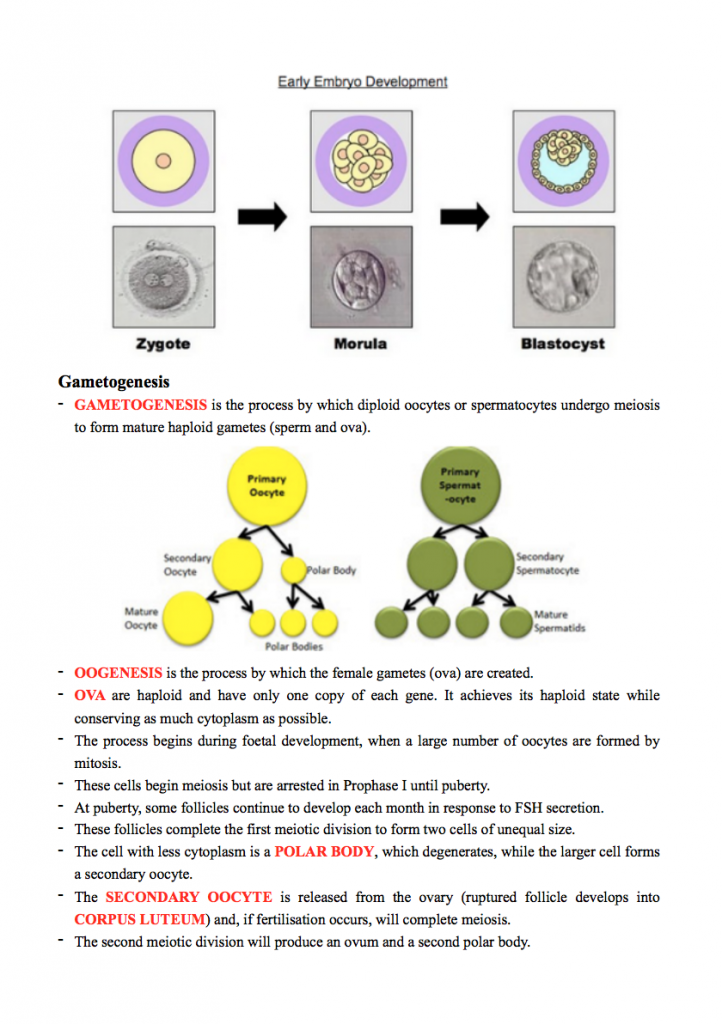
(19) Fertilisation (from ovulation to implantation, including the zygote, morula, blastocyst, trophoblast and blastocoele)
(20) Placenta (structure and function, including umbilical cord, amniotic fluid and amnion, chorionic villi, lacunae, myometrium)
(21) Foetus (vernix, foetal viability)
(22) Foetal circulation (foramen ovale, ductus arteriosus, ductus venosus, umbilical vein, umbilical artery)
(23) Effects of drugs on the foetus using examples such as neonatal abstinence syndrome and illegal opiates
(24) Birth and gestation (gestation period and importance of oxytocin)
(25) Twins (monozygotic and dizygotic twins)
(26) Reproductive technologies (in-vitro fertilisation, artificial insemination, GIFT, ZIFT, ICSI, surrogacy)
(27) Ethics of reproductive technologies
(28) Methods of contraception (IUD, condom)


Reviews