AP Chemistry
Summary:
This AP Chemistry study guide covers various topics essential for understanding advanced chemical concepts. It begins with Mass Spectroscopy of Elements, a technique used to identify isotopes of elements and calculate their average atomic mass by analyzing mass spectra. Photoelectron Spectroscopy is an experimental technique that determines the relative energies of electrons in atoms or ions. It utilizes high-energy radiation to remove electrons and is based on the Aufbau Principle. The guide also covers various types of chemical bonds – ionic, covalent, and metallic. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms and are affected by ion charge and size. Covalent bonds entail sharing electrons and can be nonpolar or polar, including sigma and pi bonds. Metallic bonds feature delocalized electrons, making metals good conductors of electricity and malleable. Bond polarity arises from differences in electronegativity between atoms. Intramolecular Forces and Potential Energy concern the balance between attractive and repulsive forces in chemical bonds. Ionic bonds are attractions between cations and anions, and Coulomb’s Law can explain their interactions. Finally, the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory states that negatively charged electrons repel each other, affecting molecular geometry based on the number of electron domains around a central atom. All these topics provide a comprehensive understanding of chemistry at the AP level.
Excerpt:
AP Chemistry
AP Chemistry Notes and Study Guide
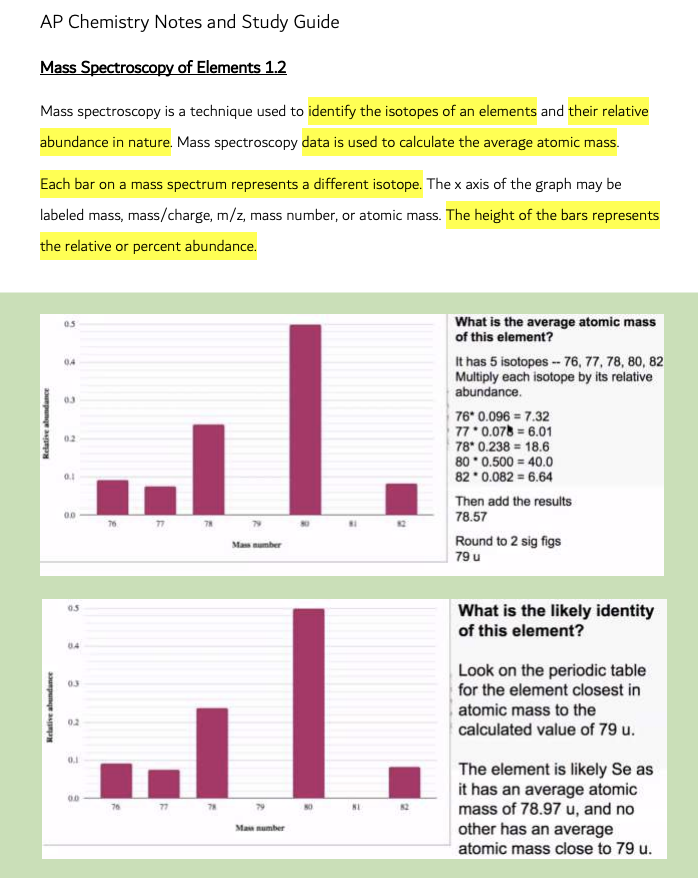
Mass Spectroscopy of Elements 1.2
Mass spectroscopy is a technique used to identify the isotopes of an element and their relative abundance in nature. Mass spectroscopy data is used to calculate the average atomic mass. Each bar on a mass spectrum represents a different isotope. The x-axis of the graph may be labelled mass, mass/charge, m/z, mass number, or atomic mass. The height of the bars represents the relative or per cent abundance.
…
Three primary types of questions:
1. Estimate atomic mass from the mass spectrum (could be a fictitious element).
2. Identify elements from the mass spectrum.
3. Identify isotope from the mass spectrum.

Reviews