Antifungal Drugs – Pharmacology Notes
Summary:
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms known for their crucial role in decomposing and recycling nutrients. They are susceptible to antifungal drugs, used extensively to combat fungal infections, especially in immunocompromised patients. The main types of antifungal drugs are antibiotics, antimetabolites, azoles, allylamines, and other topical agents. Fungal infections can vary in severity, ranging from mild to life-threatening, and can be broadly categorized into superficial mycosis, cutaneous mycosis, subcutaneous mycosis, systemic mycosis, and opportunistic mycosis. Each infection affects different parts of the body and is caused by specific types of fungi, which determine the appropriate treatment method. Superficial and cutaneous mycoses mainly affect the skin, hair, and nails, while subcutaneous mycosis occurs when fungi penetrate the skin through trauma. Systemic mycosis typically involves internal organs, primarily the respiratory system. Opportunistic mycosis results from regular human flora turning pathogenic due to compromised immune defences. Different antifungal drugs are used to treat these infections based on their efficacy against the causative fungus.
Excerpt:
Antifungal Drugs
ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS
- The drugs used for the treatment of fungal infections.
- Fungal infections are iatrogenic.
- Fungal infections are susceptible to immunocompromised patients due to chemotherapy.
- Fungal infections can range from mild to life-threatening.
- Antifungals are of two types:
- 1. Fungistatic – inhibit fungal growth.
- 2. Fungicidal – kill the fungi.
FUNGI
- Eukaryotic organisms possess a cell wall.
- They are a diverse group of Heterotrophs. Many are ecologically important Saprophytes others are Parasites.
- Do not perform photosynthesis as they lack chlorophyll.
- They are important decomposers and recyclers of nutrients in the environment.
- They are Multicellular except for Yeast.
- Produce both sexual and asexual spores.
- They are non-motile.
CELL STRUCTURE:
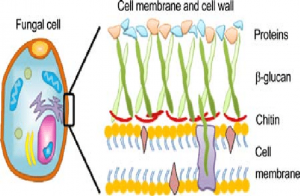
Antifungal Drugs
- The fungal cell has a rigid cell wall composed of chitin(N-acetylglucosamine), glucan and glycoproteins.
- The cell membrane contains Ergosterol, proteins and lipid.
- Most fungi have small nuclei, with little repetitive DNA.
- Other organelles, such as Mitochondria with plate-like cristae and Golgi bodies, are present.
- Ribosomes, Endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, lipids, microtubules and vesicles are found.


Reviews