All About Vitamins in Biochemistry
Summary:
As described by Bedlu Sahlu, vitamins are organic compounds present in minute amounts in natural foods, vital for metabolizing carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. They’re bifurcated into fat-soluble (A, D, E, K) and water-soluble (B complex and C) categories. Focusing on Vitamin A, its active form, is found in animal tissues, while plants offer a precursor called beta-carotene. This vitamin has various forms, with the all-trans variant predominant, and has compounds termed retinoids, like retinol and retinal. Its absorption requires bile, stored in the liver and transported to tissues bound to the retinol-binding protein (RBP). Within cells, it binds to specific proteins, affecting gene activation. Crucially, in the realm of vision, Vitamin A plays a role in the functioning of rods (responsible for dim light vision) and cones (for colour vision). Rods contain rhodopsin, a deficiency that can cause night blindness. Cones aid in colour vision, with three types, each sensitive to a specific light colour. On a biochemical level, retinoic acid, a form of Vitamin A, governs gene expression and tissue differentiation, behaving similarly to steroid hormones by binding to specific nuclear receptors.
Excerpt:
All About Vitamins in Biochemistry
Introduction
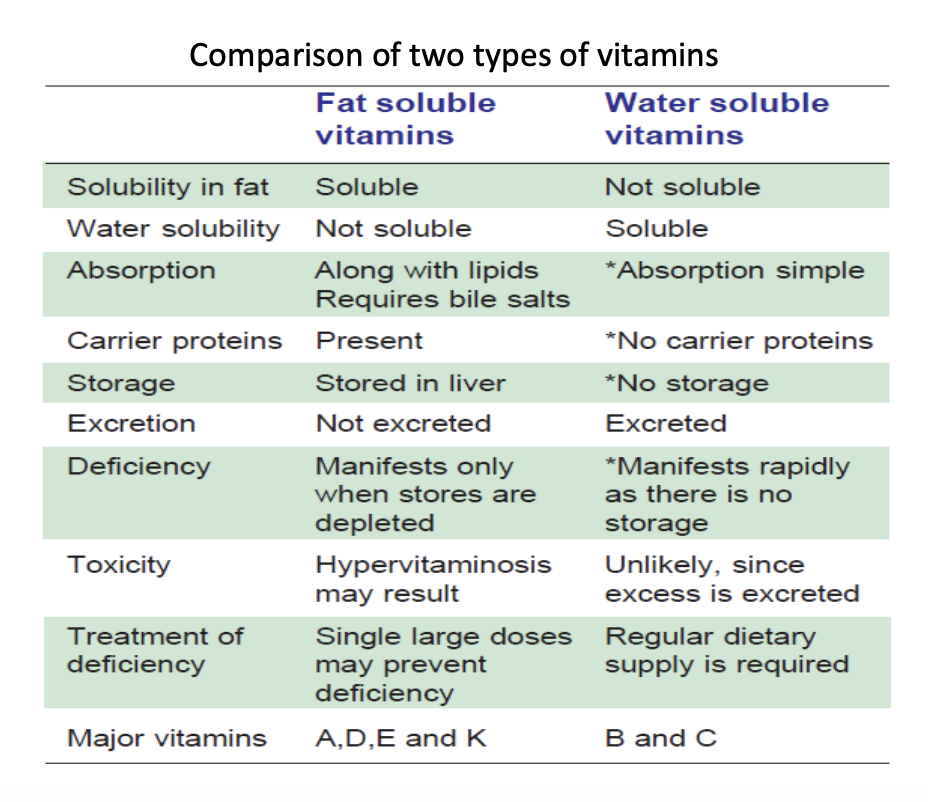
• Vitamins may be defined as organic compounds occurring in small quantities in different natural foods
• Vitamins are essential food factors that are required to properly utilise carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
• The vitamins are mainly classified into two:
1. The fat-soluble vitamins are A, D, E and K
2. Water soluble vitamins are named B complex and C
…
VITAMIN A
• The active form is present only in animal tissues.
• The pro-vitamin, beta-carotene, is present in plant tissues.
• One beta carotene molecule can theoretically give rise to two molecules of vitamin A, but it may produce only one in biological systems.
• All the compounds with vitamin A activity are referred to as retinoids.
• Three different compounds with vitamin A activity are retinol, retinal and retinoic acid (vitamin A acid)

Reviews